Discovering how to debug Python code using VSCode debugger is essential for efficient development and troubleshooting. This powerful tool streamlines the debugging process, helping developers identify issues quickly and improve code quality with minimal effort. By mastering VSCode’s debugging features, you can gain deeper insights into your code’s execution flow and resolve bugs more effectively.
This guide covers setting up the environment, managing breakpoints, inspecting variables, navigating call stacks, and utilizing advanced debugging features. Whether you’re working in virtual environments, remote setups, or handling complex asynchronous code, understanding these techniques will significantly enhance your debugging workflow.
Introduction to debugging Python code with VSCode
Debugging is an essential aspect of software development, enabling programmers to identify, analyze, and resolve errors within their code efficiently. In Python development, where dynamic typing and flexible syntax can sometimes make bugs elusive, an effective debugging process is vital for maintaining code quality and ensuring program correctness. Visual Studio Code (VSCode), a popular and versatile code editor, significantly enhances the debugging experience through its integrated debugger, offering a streamlined workflow that integrates seamlessly with Python projects.
VSCode provides a comprehensive set of core features tailored specifically for Python debugging. These include breakpoints to pause execution at critical points, variable inspection to observe program state, step-through execution to analyze code line by line, and an interactive console for real-time command input. These tools facilitate a thorough understanding of code behavior, making it easier to locate and fix issues efficiently.
Setting up debugging in VSCode involves installing the appropriate Python extension, configuring launch settings, and ensuring the environment is properly prepared with necessary dependencies and interpreter paths.
Core Features of the VSCode Debugger for Python
Understanding the core capabilities of the VSCode debugger helps developers leverage its full potential to streamline their debugging process. These features are designed to offer granular control over program execution, enabling developers to diagnose complex issues effectively.
- Breakpoints: Allow pausing program execution at specific lines or conditions, enabling examination of program state at precise moments. Developers can set simple breakpoints, conditional breakpoints that activate based on variable values, or function breakpoints to pause whenever a particular function is invoked.
- Variable Inspection and Watch: Provide real-time visibility into the current values of variables and expressions during paused states. The Watch panel allows continuous monitoring of specific variables or expressions, aiding in understanding how data evolves through execution.
- Step Execution: Offers precise control with options to step over, into, or out of lines of code. This granular approach helps trace the flow of execution, isolate problematic sections, and understand the impact of each line on program state.
- Call Stack Navigation: Displays the sequence of function calls leading to the current pause point. Navigating the call stack helps identify how the program arrived at a particular state and isolates faulty function calls.
- Interactive Debug Console: Enables executing Python commands in the current debugging context. This feature allows on-the-fly testing of hypotheses or inspecting objects without modifying the source code.
- Conditional and Hit Count Breakpoints: Enable more nuanced debugging by pausing execution only when specific conditions are met or after a breakpoint has been hit a certain number of times, optimizing debugging sessions for particular scenarios.
Prerequisites for Setting Up Debugging in VSCode
Proper setup ensures a smooth debugging experience, minimizing configuration issues and enabling immediate productivity. The prerequisites include installing essential extensions, configuring launch.json files, and preparing the Python environment.
- Python Extension for VSCode: Installing the official Python extension from the Visual Studio Code marketplace is crucial, as it provides language support, IntelliSense, and debugging capabilities tailored specifically for Python.
- Python Interpreter Configuration: Selecting the correct Python interpreter ensures that the debugger runs within the desired environment, whether it’s a system-wide Python installation, virtual environment, or conda environment. This is configured through VSCode’s interpreter selection command.
- Debugging Configuration Files: Creating or editing the launch.json configuration file within the .vscode directory allows customization of debugging parameters. Typical settings include specifying the script to run, environment variables, command-line arguments, and debugger options.
- Ensuring Dependencies and Environment Setup: Verifying that all required packages and modules are installed and accessible within the selected interpreter prevents runtime errors during debugging sessions. This includes installing dependencies via pip or conda, and ensuring environment variables are correctly set.
- Workspace and File Structure: Organizing your project files properly facilitates easier debugging. Opening the root project folder in VSCode ensures that relative paths and environment settings function correctly during debugging.
By fulfilling these prerequisites, developers can harness the full power of VSCode’s debugging tools, resulting in a more efficient development cycle and higher-quality Python applications.
Setting up the VSCode environment for Python debugging
Establishing a well-configured Visual Studio Code environment is essential for efficient Python debugging. Proper setup not only facilitates seamless debugging sessions but also enhances productivity through organized project management and tailored configurations. This section Artikels the necessary steps to install the Python extension, configure debugging settings, and maintain an organized workspace that supports effective troubleshooting.
By following these guidelines, developers can create a robust environment that simplifies the debugging process, minimizes setup time, and ensures consistency across different projects and debugging scenarios. The focus is on leveraging VSCode’s powerful features to streamline workflows and improve code quality through systematic debugging practices.
Installing the Python extension in Visual Studio Code
The first step toward a productive debugging environment in VSCode involves installing the official Python extension, which provides essential features such as syntax highlighting, code completion, linting, and debugging support. Ensuring this extension is properly installed sets the foundation for all subsequent configuration and debugging activities.
- Open Visual Studio Code on your computer.
- Navigate to the Extensions view by clicking on the Extensions icon in the Activity Bar on the side or by pressing Ctrl+Shift+X.
- In the search bar, type “Python” to locate the official Python extension provided by Microsoft.
- Select the extension titled “Python” from the search results. Verify that it is published by Microsoft to ensure authenticity.
- Click on the “Install” button. The extension will download and install automatically, which might take a few moments.
- Once installed, the extension activates immediately, enabling features like IntelliSense, linting, and debugging for Python files.
To confirm successful installation, open a Python script and check if the Python-specific features like code completion and syntax highlighting are active. You can also verify installed extensions by navigating to the Extensions view and ensuring the Python extension shows as enabled.
Configuring the launch.json file for debugging scenarios
Customizing the launch.json file allows developers to define specific debugging configurations suited to different project structures or debugging needs. Proper configuration ensures that debugging sessions are accurate, efficient, and tailored to the context of the codebase.
Visual Studio Code provides a guided setup for creating this configuration file, which can be further refined for complex scenarios such as remote debugging, multi-file projects, or variable environment setups.
- Open the Command Palette by pressing Ctrl+Shift+P or Cmd+Shift+P on macOS.
- Type “Debug: Open launch.json” and select the command. If this is your first configuration, VSCode will prompt you to select an environment.
- Select “Python” from the list of environments. This action creates a default
launch.jsonfile with baseline settings. - Review and modify the generated configurations based on your specific debugging scenario. Common configurations include:
| Scenario | Configuration Details |
|---|---|
| Running a single script |
|
| Debugging with command-line arguments |
|
| Remote debugging |
|
Adjust the parameters like program, args, and connect to match your project’s structure and debugging requirements. Saving these configurations allows for quick setup of debugging sessions aligned with different project scenarios.
Organizing the project workspace for effective debugging
An organized workspace significantly reduces debugging time and prevents common pitfalls such as misconfigured paths or overlooked dependencies. Proper project organization ensures that the debugging process is smooth, intuitive, and reproducible across different environments and team members.
Key best practices include the following:
- Maintain a clear directory structure that separates source code, tests, configurations, and documentation. For example, use folders like
src,tests, andconfig. - Use a dedicated
settings.jsonfile within the.vscodedirectory to store workspace-specific configurations, such as environment variables or interpreter paths. - Configure environment variables and interpreter paths within the
settings.jsonorlaunch.jsonto ensure consistency during debugging sessions. - Leverage virtual environments for dependency management, and specify the interpreter path explicitly in VSCode settings to avoid discrepancies.
- Integrate relevant testing and linting tools, like pytest or flake8, into the workspace, so they work seamlessly with debugging activities.
By maintaining a clean and predictable workspace structure, developers can quickly locate files, streamline debugging workflows, and reduce the likelihood of configuration errors that hinder troubleshooting efforts.
Creating and Managing Breakpoints in VSCode
Breakpoints are essential tools in debugging that allow developers to pause program execution at specific points, enabling inspection of variable states and program flow. Mastering how to effectively set, control, and manage breakpoints within VSCode enhances the debugging experience, making it easier to identify and resolve issues in Python code.
VSCode provides a flexible environment for managing breakpoints with various options to customize debugging sessions according to specific needs. Understanding the different types of breakpoints and how to manipulate them within the editor and Breakpoints panel can significantly streamline the debugging process.
Adding, Enabling, Disabling, and Removing Breakpoints
Efficient breakpoint management starts with knowing how to add and control them directly within the VSCode editor. Breakpoints are typically set by clicking in the gutter area next to the line numbers, which toggles the breakpoint on that line. Once placed, breakpoints can be enabled or disabled, offering flexibility during different debugging phases.
Breaking down the process:
- Adding breakpoints: Click on the gutter next to the desired line, or press
F9with the cursor on the line to toggle a breakpoint. The breakpoint appears as a red dot. - Enabling/Disabling breakpoints: Right-click on an existing breakpoint or use the command palette (
Ctrl+Shift+P) to toggle its enabled state. Disabled breakpoints are grayed out, indicating they won’t pause execution. - Removing breakpoints: Click again on the red dot or right-click and select ‘Remove Breakpoint.’ Alternatively, use the Breakpoints panel to remove multiple breakpoints at once.
These simple actions allow developers to control where the debugger pauses, facilitating focused investigation of specific code sections.
Types of Breakpoints and Their Use Cases
Beyond standard breakpoints, VSCode offers various specialized types, each suited for different debugging strategies. Utilizing these enhances the ability to monitor specific conditions, logs, or code execution flows without cluttering the codebase with print statements.
| Type of Breakpoint | Description | Common Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| Conditional Breakpoints | Pauses execution only when a specified condition evaluates to true. Conditions are written as expressions in the language of the program. | Debugging loops or functions where the issue occurs only under certain data states, e.g., counter > 10 or user.id == 100. |
| Logpoints | Instead of pausing execution, logpoints insert logs at specific lines, helping track variables or execution flow without interruption. | Monitoring variable values over iterations or tracing code paths in complex workflows. |
| Function Breakpoints | Set breakpoints that trigger whenever a particular function is called, regardless of where it is located in the codebase. | Tracking how often or under what circumstances a specific function executes, useful in large projects with many function calls. |
Each breakpoint type serves a specific purpose, allowing tailored debugging sessions that reduce unnecessary pauses or verbose logs, making troubleshooting more efficient.
Managing Breakpoints in the Breakpoints Panel
The Breakpoints panel in VSCode centralizes control over all breakpoints set during a debugging session. It provides an overview of their status, type, and conditions, enabling developers to manage multiple breakpoints effectively.
- Accessing the panel: Open the Debug view (
Ctrl+Shift+D) and select the ‘Breakpoints’ section to view all active breakpoints. - Enabling/disabling: Toggle the checkbox next to each breakpoint to enable or disable it without removing it entirely.
- Editing conditions: Right-click a breakpoint and choose ‘Edit Condition’ to specify or modify the condition expression for conditional breakpoints.
- Removing breakpoints: Use the trash icon or right-click options to delete individual breakpoints or clear all at once, maintaining a clean debugging environment.
Managing breakpoints through this panel allows for quick adjustments, especially during iterative debugging sessions, providing a comprehensive overview that simplifies controlling complex debugging workflows.
Using the VSCode Debugger Controls Effectively
Mastering the debugger controls within Visual Studio Code enhances the efficiency and precision of troubleshooting Python code. These controls allow developers to navigate through code execution seamlessly, identify issues swiftly, and understand program flow more comprehensively. Effectively leveraging these tools can significantly reduce debugging time and improve code quality.
VSCode provides a suite of debugger controls accessible through both the debug toolbar and keyboard shortcuts. Understanding how to utilize these controls optimally ensures smooth debugging sessions, enabling developers to pause, inspect, and resume code execution systematically. Proper management of these controls is essential for isolating bugs, testing fixes, and maintaining productive debugging workflows.
Controlling Debugging Sessions with the Debug Toolbar and Keyboard Shortcuts
During a debugging session, the debug toolbar offers intuitive buttons to manipulate code execution. Familiarity with these controls and their keyboard equivalents allows for efficient navigation without distracting from the development process.
| Control | Description | Keyboard Shortcut |
|---|---|---|
| Start/Continue | Begins the debugging session or resumes execution until the next breakpoint or end of program. | F5 |
| Pause | Pauses the current execution, allowing inspection of variables and program state. | F6 or Ctrl+Shift+F5 |
| Stop | Ends the debugging session entirely, closing the debugging process. | Shift+F5 |
| Restart | Restarts the debugging session from the beginning, useful after making changes to code. | Ctrl+Shift+F5 |
| Step Over | Executes the current line of code and moves to the next line, skipping over function calls. | F10 |
| Step Into | Enters into functions called at the current line, allowing line-by-line debugging within functions. | F11 |
| Step Out | Completes execution of the current function and returns to the caller, resuming debugging there. | Shift+F11 |
Utilizing these controls efficiently involves not only knowing their functions but also practicing their use during debugging sessions. The debugger toolbar provides visual cues and immediate access, while keyboard shortcuts enable rapid control flow management without interrupting the debugging process.
For example, pressing F5 resumes execution until hitting another breakpoint or completion. Using F10 allows developers to execute one line at a time, ideal for closely inspecting variable states. Shift+F11 offers a quick way to exit the current function scope, returning focus to the calling context. Combining these controls strategically helps in dissecting complex issues within the code efficiently.
When a debugging session needs to be halted or restarted, the ‘Stop’ (Shift+F5) and ‘Restart’ (Ctrl+Shift+F5) buttons provide clean termination and reinitialization of the process, ensuring that the environment resets correctly and no lingering states affect subsequent debugging.
Inspecting Variables and Expressions During Debugging
Effective debugging in Python relies heavily on the ability to inspect variables and evaluate expressions dynamically. During a debugging session in VSCode, developers can gain real-time insights into the program’s state, helping identify logical errors, incorrect data, or unexpected behavior. Understanding how to view and interpret variable values and expressions enhances debugging efficiency and accuracy, enabling a more streamlined process toward resolving issues.Inspecting variables and evaluating expressions is crucial because it provides immediate visibility into the internal data without altering the code.
This process helps developers pinpoint exactly where and why a bug manifests, especially in complex programs with numerous variables and intricate logic. Being adept at leveraging VSCode’s debugging tools allows for a deeper understanding of program flow, making the development process more robust and reliable.
Viewing Variables in the Debug Console and Variables Pane
During a debugging session, the most straightforward method to monitor the state of your program involves examining variables through the VSCode interface. The Variables pane and Debug Console serve as primary tools for this purpose.The Variables pane offers a hierarchical view of all local, global, and, if applicable, watch variables in scope at the current breakpoint. Local variables are immediately visible, showing the current function’s data, while global variables reflect the broader application state.
Developers can expand these entries to explore nested data structures such as lists, dictionaries, and custom objects, providing a comprehensive snapshot of the program’s current state.The Debug Console complements this by displaying output generated during the debugging process and allowing interactive evaluation of expressions. By typing variable names or expressions into the console, users can observe their current values. This is particularly useful for ad-hoc checks or verifying the results of specific computations without modifying the codebase.
Both tools facilitate a clear understanding of how variables evolve as the program executes, enabling precise diagnosis of issues.
Evaluating Expressions Dynamically in a Debugging Session
Evaluating expressions during debugging offers the flexibility to test hypotheses, verify computations, or inspect the result of complex expressions without altering the source code. VSCode’s debugger allows users to evaluate any valid Python expression in the current scope dynamically.To evaluate expressions, simply select or type an expression into the Debug Console and press Enter. The debugger will execute the expression in the current context and display the result immediately.
This capability is particularly useful when debugging conditional logic, checking the value of computed variables, or dynamically testing alternative code snippets.For example, to verify the value of an element in a list, inputting `my_list[2]` will return the third element, helping confirm whether the data is as expected. For more complex expressions, combining multiple variables or applying functions directly within the console provides a powerful tool to understand the program’s behavior without making permanent code modifications.This dynamic evaluation promotes an interactive debugging experience, where developers can iteratively explore and diagnose issues efficiently.
Using Hover Tooltips for Quick Variable Inspection
Hover tooltips present an intuitive and immediate method for inspecting variable states during debugging sessions in VSCode. When the debugger pauses at a breakpoint, simply hovering the mouse cursor over a variable or an expression in the code reveals a popup tooltip displaying its current value.This feature allows for quick, context-sensitive insights without switching views or expanding panes. It is especially useful for getting a rapid snapshot of variable data at critical points in the code, such as within conditional statements or complex functions.
The hover tooltip provides a non-intrusive way to verify variable states without interrupting the debugging flow.Moreover, the tooltips can display not only simple data types but also more complex structures, such as dictionaries or objects, often with expandable details. Utilizing this feature effectively saves time and improves clarity when tracking variable changes, making debugging a more seamless and user-friendly process.
Managing the Call Stack and Navigation
Understanding and effectively navigating the call stack during debugging is essential for tracing the execution flow of your Python program. The call stack provides a snapshot of all active function calls at any point during program execution, enabling developers to diagnose issues, identify where errors originate, and analyze the sequence of function invocations leading to a bug.
By managing the call stack within VSCode’s debugger, you can move seamlessly between different frames, inspect variables at various levels, and gain a comprehensive view of your code’s runtime behavior. Proper utilization of this feature enhances your debugging efficiency and provides deeper insights into complex code interactions.
Analyzing the Call Stack to Trace Code Execution Flow
The call stack view displays a list of frames representing each active function call, starting from the initial entry point at the top down to the current execution point. Analyzing this hierarchy allows you to understand how the program reached its current state, identify recursive calls, or locate unexpected function invocations that may contribute to bugs.
When pausing execution at a breakpoint or during a step-through, the debugger captures the current call stack. Examining this chain reveals the sequence of function calls, including parameters passed and return points. This visualization helps identify logical errors, infinite recursion, or unanticipated code paths, especially in complex applications with multiple nested functions.
Navigating Between Different Frames within the Call Stack
Efficient navigation between frames is crucial for inspecting variables and understanding the context of each function call. VSCode’s debugger provides a call stack panel where you can click on any frame to switch the context. This action updates the editor window to show the source code of the selected frame and allows variable inspection within that scope.
To navigate effectively:
- Click on a specific frame in the call stack panel to view local variables and the current line of execution in that function.
- Use keyboard shortcuts to move up or down the call stack quickly, such as the “Up” and “Down” arrow keys when the focus is on the call stack panel.
- Right-click on a frame for additional options, like setting a temporary breakpoint at the frame’s location or viewing the caller’s caller.
This flexibility ensures you can investigate multiple levels of execution without losing track of the broader call context, aiding in pinpointing where issues originate.
Setting Up the Call Stack View for Easier Debugging
Optimizing the call stack view enhances navigation and clarity during debugging sessions. VSCode allows customization of the debugger interface to suit your workflow:
| Tips for Effective Call Stack Management |
|---|
|
Additionally, familiarity with the debugger’s view options and customizing the layout of panels can streamline your debugging process, making it more intuitive to analyze and navigate through the code execution flow.
Using watch expressions and data tips

Effective debugging in Visual Studio Code involves not only setting breakpoints and inspecting variables but also actively monitoring specific expressions or variables during program execution. Watch expressions and data tips serve as invaluable tools that allow developers to keep a close watch on critical aspects of their code without cluttering the debugging interface. Mastering their use enhances debugging efficiency, especially in complex scenarios where multiple variables influence program behavior.
Watch expressions enable you to specify particular variables or expressions that you want to observe continuously as your code runs. Data tips, on the other hand, offer instant insights into variable values directly within the code editor when you hover over them during a debugging session. Together, these tools facilitate a deeper understanding of the program’s state at any given moment, allowing for quicker identification of issues and more precise troubleshooting.
Adding and Managing Watch Expressions
In the context of complex debugging sessions, organizing your watch expressions effectively can significantly streamline your workflow. To add a watch, open the Debug sidebar and locate the “Watch” panel. Click on the “Add Expression” button or directly type your variable or expression into the watch list. For example, monitoring the value of a variable like user_input or an expression such as len(items) can provide real-time updates on their current state.
Managing these watches involves editing, removing, or grouping expressions to keep your debugging view concise. You can edit a watch expression by clicking on it and modifying the text, or remove it entirely if it’s no longer relevant. For complex sessions, organizing watches into groups or categories can help you quickly locate the most important variables or expressions, especially when dealing with large data structures or nested objects.
Organize watches logically to match the flow of your code. For instance, group all variables related to user input together, and separate those handling data processing. This approach reduces cognitive load during debugging and helps you focus on the most critical elements.
Interpreting Data Tips for Quick Insights
Data tips appear as floating tooltips when you hover over a variable or expression in the code editor during a paused debugging session. They provide immediate, context-sensitive information about variable values, including primitive data types, collections, and object properties. This quick insight allows you to assess the current state of variables without switching views or expanding watch panels.
To interpret data tips effectively, consider the following strategies:
- Look for the displayed value clearly and verify it matches your expectations based on your program’s logic.
- If the data tip shows a complex object, expand it to explore nested properties and understand the object’s full state.
- Compare data tip values with corresponding watch expressions to cross-verify information and uncover discrepancies.
In cases involving large data structures or collections, data tips can be customized or filtered to display only relevant information, reducing clutter. Using data tips strategically helps in pinpointing issues quickly, especially when variables are dynamically changing or when debugging recursive functions or deeply nested objects.
Effective use of data tips can reduce the need to add numerous watch expressions, saving you time and focusing your attention on the most dynamic or complex parts of your code.
Strategies for Organizing Watches in Complex Debugging Sessions
During intricate debugging sessions involving multiple variables and complex data, organizing watch expressions becomes essential for maintaining clarity. Prioritize watches that are most critical to the current problem, and group related expressions for easier access. Consider creating logical categories, such as input parameters, intermediate calculations, and output results.
To maintain an organized watch list:
- Regularly review and prune watches that are no longer relevant to avoid clutter.
- Name your expressions clearly, especially when adding custom evaluations or functions, so their purpose is immediately understandable.
- Use comments or labels within your code to annotate the importance or expected behavior of specific variables, making it easier to correlate them with your watch expressions.
- Leverage the grouping or filtering features in VSCode’s watch panel to focus only on the subset of variables pertinent to the current debugging context.
Implementing these organizational strategies ensures that debugging remains manageable, even as the complexity of your codebase grows. It allows you to quickly locate critical information, interpret data efficiently, and make informed decisions during troubleshooting.
Configuring debugging for different Python environments
Effective debugging in Python requires proper configuration tailored to the specific environment in which the code runs. Whether working within virtual environments, Docker containers, or remote interpreters, setting up the correct debugging context ensures seamless development and troubleshooting. Proper environment setup also minimizes discrepancies between development and production or deployment setups, leading to more reliable and maintainable code.
This section provides guidance on configuring VSCode to debug Python code across various environments, highlighting key differences and best practices for each scenario.
Debugging within Virtual Environments
Virtual environments are commonly used to isolate project dependencies, preventing conflicts between packages. Debugging code inside a virtual environment in VSCode involves ensuring that the IDE uses the correct interpreter associated with that environment. This guarantees that the debugger can access all necessary libraries and dependencies.
- Activate the virtual environment in your terminal before launching VSCode, or select the interpreter in VSCode’s Command Palette using “Python: Select Interpreter” and choosing the environment from the list.
- Modify your launch configuration in the “launch.json” file to specify the interpreter path explicitly if necessary, using the
"pythonPath"attribute. - Verify that the debugger uses the intended environment by checking the interpreter displayed in the Debug Console and ensuring that installed packages are accessible during debugging sessions.
Additionally, keep in mind that virtual environments may differ across projects, so maintaining consistent configurations helps streamline debugging efforts.
Debugging within Docker Containers
Debugging Python code inside Docker containers involves connecting VSCode’s debugger to the container’s environment. This setup is pivotal when developing in containerized environments or testing deployment scenarios.
To facilitate debugging inside Docker:
- Ensure the container runs with the necessary debugging tools, such as the
ptvsdordebugpypackage, installed and configured to listen for debugger connections. - Expose the debug port in your container configuration to allow communication between VSCode and the container. Typically, this involves adding
-p 5678:5678in your Docker run command. - Configure your
launch.jsonin VSCode to attach to the running container using the"host"and"port"parameters that correspond to the exposed debug port. - Use the VSCode Remote – Containers extension for seamless integration, which enables attaching the debugger directly to the containerized environment.
Properly setting up these configurations ensures that debugging performance remains smooth, and you can step through code as if it were running locally.
Remote Debugging via SSH and Remote Interpreters
Remote debugging is essential for working with code on remote servers, cloud instances, or environments where local setup is impractical. Setting up remote interpreters and SSH connections allows developers to debug code in these environments with minimal friction.
For SSH-based remote debugging:
- Configure your
launch.jsonto specify the remote host, SSH credentials, and interpreter path on the remote machine. - Use the VSCode Remote – SSH extension to establish a connection to the remote environment, enabling the IDE to operate directly on the remote filesystem.
- Ensure the remote Python environment has the debugging packages installed (like
debugpy) and is configured to accept debugger connections. - Launch the debugger in attach mode, specifying the remote host and port where the debugger listens.
When working with remote interpreters, it’s crucial to synchronize your environment configurations, including dependencies and environment variables, to prevent inconsistencies during debugging. Using remote containers or SSH tunneling can further streamline this process.
Handling Environment-Specific Configurations
Managing environment-specific configurations effectively ensures that debugging remains reliable across diverse setups. This involves defining clear settings for interpreters, dependencies, and debugging parameters tailored to each environment.
- Maintain distinct
launch.jsonconfigurations for each environment, specifying interpreter paths, environment variables, and debugging ports as needed. - Use environment variables or configuration files to dynamically adjust behavior based on the environment, such as database credentials or API keys.
- Leverage VSCode’s multi-root workspace feature to manage multiple environments within a single project, simplifying configuration management.
- Ensure consistency in dependency versions across environments by using lock files like
requirements.txtorpipfile.lock, preventing unexpected issues during debugging sessions.
Adopting these practices reduces environment-related errors and enhances the robustness of the debugging process, making it easier to troubleshoot and resolve issues efficiently regardless of the deployment context.
Handling Exceptions and Errors During Debugging
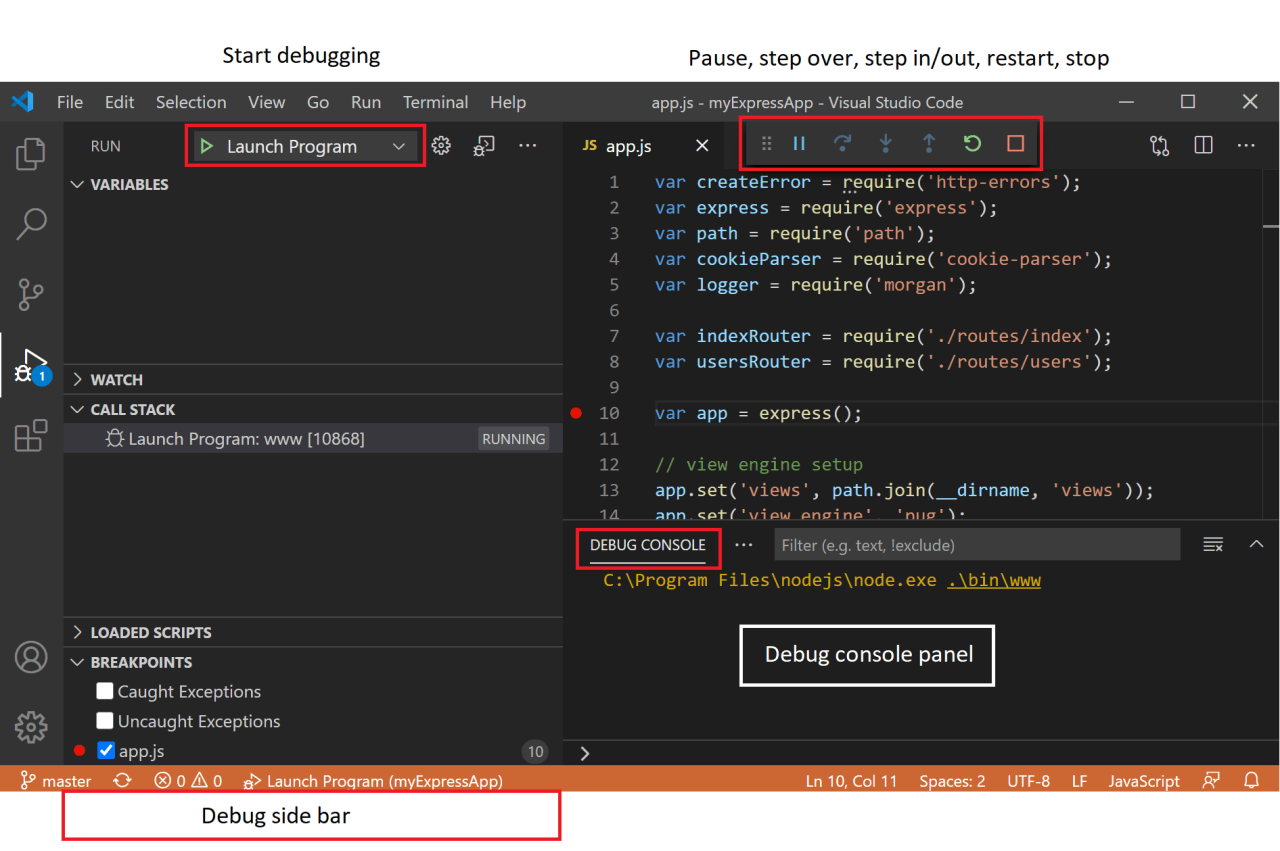
Effective debugging in Python requires not only identifying issues but also understanding how exceptions and errors are raised and handled within the code. Visual cues provided by VSCode significantly enhance the debugging experience by highlighting exceptions and errors directly in the editor. This section explores how VSCode assists developers in recognizing, configuring, and inspecting exceptions to streamline troubleshooting processes.
When working with complex applications, exceptions can occur unexpectedly, interrupting the flow of execution. Recognizing these issues promptly is crucial for efficient debugging. VSCode’s debugger offers visual indicators that mark unhandled exceptions, making it easier to pinpoint problematic code segments. Additionally, configuring breakpoints to trigger on specific exceptions or error conditions provides targeted control over the debugging process, facilitating a more focused investigation of issues.
Understanding how to visually inspect traceback information further empowers developers to trace the root cause of errors systematically, especially in complex call stacks or multi-threaded environments.
Visual Highlighting of Exceptions and Errors in VSCode
VSCode enhances error detection by visually marking exceptions directly in the editor. When an exception occurs during debugging, the affected line is highlighted with a distinctive color—typically red—to draw immediate attention. This visual cue is complemented by an inline message or tooltip that displays the error message or exception type, providing instant insight into the nature of the problem. If the exception is unhandled, VSCode may also display a notification or expand the call stack panel with relevant traceback details.
Moreover, as you step through code, VSCode can break on specific exceptions, pausing execution precisely at the line where an error is raised. This capability allows for an in-depth examination of variable states and control flow at the moment of failure, significantly simplifying error diagnosis.
Configuring Breakpoints to Trigger on Exceptions or Specific Error Conditions
Configuring breakpoints to activate upon encountering exceptions offers granular control over the debugging process. VSCode provides an option to set “Break on Exception” within the debug configuration, enabling developers to specify whether to break on all exceptions, only unhandled exceptions, or specific error types. This feature ensures that the debugger pauses precisely when a problematic error occurs, allowing for immediate inspection and diagnosis.
To set this up, access the debug settings and modify the configuration file or use the “Break on Exception” toggle in the debugger toolbar. For more granular control, developers can leverage conditional breakpoints that activate only when certain error messages or traceback patterns are detected, such as specific error codes or exception messages. This approach minimizes unnecessary pauses and focuses debugging efforts on critical issues.
Inspecting Traceback Information Visually
Traceback information is vital for understanding the sequence of function calls leading to an exception. VSCode’s debugger displays traceback details in the “Call Stack” panel, offering a hierarchical view of active frames at the point of failure. Developers can expand each frame to inspect local variables, arguments, and execution context within each function call, facilitating a comprehensive understanding of how an error propagated through the code.
Additionally, VSCode supports hover-over tooltips and data tips that reveal variable values and expressions directly within the editor during debugging sessions. When examining traceback data, it is helpful to review the sequence of calls from the initial invocation to the point of exception, identifying which function or line introduced the error. This visual approach accelerates troubleshooting by providing immediate access to relevant context and variable states at each step of the call stack.
Using Advanced Debugging Features
Leveraging advanced debugging techniques in Visual Studio Code enhances the efficiency and effectiveness of the development process. These features allow developers to perform nuanced inspections, control program execution with greater precision, and troubleshoot complex issues such as concurrency and asynchronous operations. Mastering these tools empowers programmers to diagnose problems more rapidly and understand intricate code behaviors without intrusive modifications or excessive logging.
By utilizing conditional breakpoints, logpoints, inline expression evaluations, and specialized handling for multi-threaded and asynchronous code, developers can elevate their debugging strategies. These features facilitate more targeted investigations and streamline the debugging workflow, especially in complex Python applications that involve concurrent processes or asynchronous tasks.
Setting Conditional Breakpoints Based on Variable States
Conditional breakpoints enable stopping program execution only when specific conditions related to variable states are met. This feature prevents unnecessary pauses and focuses debugging efforts on the exact scenarios where issues manifest, greatly enhancing debugging efficiency in complex programs.
- Right-click on an existing breakpoint or click in the gutter next to the line number to create a breakpoint.
- Select the “Edit Breakpoint” option or click the gear icon associated with the breakpoint.
- Enter a Boolean expression in the condition field, such as
variable_name > 10
, or a more complex logical expression involving multiple variables.
- Ensure that the expression is valid Python syntax. The debugger evaluates the condition each time the breakpoint is reached.
- The debugger pauses execution only if the condition evaluates to true, allowing for pinpointed inspection of specific states or data conditions.
Conditional breakpoints are particularly useful for tracking down elusive bugs that occur under specific data conditions or after certain operations have executed multiple times. They reduce the need for inserting numerous print statements or manual checks, maintaining cleaner code and a more streamlined debugging process.
Utilizing Logpoints for Non-Intrusive Logging During Execution
Logpoints are an advanced feature that allows developers to insert logging statements into the code without modifying the source files. During debugging sessions, logpoints output messages to the debug console, providing real-time insights into program flow and variable states, while avoiding the interruptions caused by breakpoints.
- Click in the gutter next to the line where you want to insert a logpoint.
- Right-click and select “Add Logpoint,” or press the appropriate shortcut to create one.
- Specify the log message, which can include expressions enclosed in curly braces, such as
Processing item: item_id
.
- Configure the log message to include multiple variable values, timestamps, or other contextual information to facilitate comprehensive monitoring.
- Run the debugger; messages will appear in the debug console when the execution reaches the logpoint, without pausing the program.
Using logpoints is especially advantageous in production-like environments or when debugging long-running processes, as they enable continuous observation without halting execution or altering code behavior significantly.
Inline Expression Evaluation and Data Visualizations
Inline expression evaluation allows developers to assess variable values and expressions directly within the editor during a debugging session. This feature provides immediate insights into the data without the need for separate print statements or external tools.
- Hover over variables or expressions while paused at a breakpoint to view their current values in a tooltip.
- Use the inline evaluation widget in the editor to add expressions for real-time monitoring.
- Right-click on variables and select options such as “Add to Watch” for continuous tracking.
Data visualizations during debugging, such as inline charts or tables, are supported via extensions or integrated tools. For example, visualizing large datasets or nested data structures helps comprehend complex data flows or identify anomalies more intuitively. Advanced features may include inline graphs or heatmaps of variable states, providing a richer context in real-time.
Debugging Multi-Threaded and Asynchronous Python Code
Handling multi-threaded and asynchronous code presents unique challenges, requiring specialized debugging approaches to understand concurrent behaviors and race conditions effectively. VSCode offers tools and strategies to manage these complexities:
- Thread Management: The debugger interface displays active threads, allowing developers to select and inspect individual threads separately. Use the Threads panel to switch focus, set thread-specific breakpoints, and analyze thread-specific call stacks.
- Async Support: When debugging asynchronous code using
asyncandawait, the debugger preserves the asynchronous call context. You can set breakpoints on await points and step through asynchronous functions to trace execution flow accurately. - Breakpoints and Conditions: Set thread-specific or async-specific breakpoints to target particular execution paths or concurrent tasks.
- Visualizing Concurrency: Use VSCode extensions or built-in features to visualize thread activity, task queues, and event loops, providing clearer insights into concurrency issues.
- Synchronization Techniques: Employ synchronization primitives like locks and semaphores during debugging to analyze potential deadlocks and race conditions.
Effective debugging of multi-threaded and asynchronous code involves understanding the interplay between concurrent tasks, managing breakpoint placement across threads, and carefully analyzing call stacks in different contexts. These capabilities enable developers to diagnose intricate issues related to timing, deadlocks, and asynchronous event handling with confidence.
Summary
Mastering how to debug Python code using VSCode debugger empowers developers to write cleaner, more reliable code while reducing troubleshooting time. With its comprehensive set of tools and best practices, VSCode becomes an invaluable companion in your development journey, enabling you to diagnose and fix issues with confidence and precision.