Deploying a React application to Vercel for free offers a seamless way to host your projects with minimal hassle and optimal performance. Vercel’s free tier provides essential features that make it an excellent choice for developers looking to showcase their React apps without incurring costs.
This guide walks you through the entire process, from preparing your React project and setting up a Vercel account to configuring deployment settings and managing updates, ensuring your application goes live smoothly and efficiently.
Overview of deploying React applications to Vercel for free

Deploying React applications to Vercel offers a streamlined, efficient, and cost-effective way to deliver interactive web experiences. As a platform optimized for frontend frameworks like React, Vercel simplifies the deployment process, enabling developers to focus on building features rather than managing infrastructure. The free tier of Vercel provides ample resources for individual developers, hobby projects, and small teams to host and update their React applications without incurring costs.
This overview explores the advantages of using Vercel for React deployment, suitable project types for this environment, and a high-level summary of the deployment workflow that ensures quick and reliable publishing of your applications.
Benefits of using Vercel for React deployment
Vercel’s free tier offers numerous features tailored specifically for frontend projects, making it an attractive platform for React developers. These benefits include:
- Global CDN Integration: Content is automatically distributed across a worldwide Content Delivery Network, ensuring fast load times regardless of user location.
- Automatic Builds and Deployments: Integration with version control systems like GitHub, GitLab, and Bitbucket enables automatic deployment workflows upon code commits.
- Serverless Functions: Support for serverless backend functions allows developers to extend React apps with backend logic without managing servers.
- Easy Configuration: Minimal configuration is required to deploy a React application, often just connecting a repository and setting environment variables.
- Free Tier Limits: The free plan includes generous bandwidth and build minutes suitable for personal projects, prototypes, and small-scale applications.
Suitable React applications for deployment on Vercel
Vercel is ideal for a broad range of React applications, especially those that benefit from rapid deployment, scalability, and global reach. Suitable projects include:
- Single-page applications (SPAs) that rely on client-side rendering for dynamic content.
- Static React sites generated using frameworks like Next.js, Gatsby, or Create React App with static export.
- Prototypes and MVPs that need quick deployment and easy iteration.
- Small to medium-scale projects that require high availability and fast performance without extensive backend infrastructure.
High-level deployment process for React applications on Vercel
Deploying a React application on Vercel involves a series of straightforward steps, designed to minimize setup time and maximize efficiency. The general workflow includes:
- Connecting Your Repository: Link your GitHub, GitLab, or Bitbucket repository containing your React project to Vercel.
- Configuring Build Settings: Specify the build command (e.g., ‘npm run build’) and the output directory (commonly ‘build’ or ‘dist’) in Vercel’s dashboard.
- Initiating Deployment: Vercel automatically triggers the build process upon repository connection or code push, generating a production-ready version of your React app.
- Reviewing Deployment: Check the live preview link provided by Vercel to verify your application functions correctly.
- Publishing: Once satisfied, deploy the application to the production environment with a single click or automatically through configured branches.
This simplified process allows developers to deploy updates rapidly, benefiting from Vercel’s infrastructure and continuous deployment capabilities for a seamless development-to-production pipeline.
Preparing a React Application for Deployment
Before deploying a React application to Vercel, it is essential to ensure that the project is properly configured and optimized. Proper preparation not only facilitates a smooth deployment process but also enhances application performance and maintainability. This stage involves setting up build scripts, adjusting configurations, and implementing best practices to optimize the app for production use.
Effective preparation includes managing environment variables, optimizing the codebase for performance, and organizing project files systematically. These steps ensure that the deployment process is efficient and that the application performs reliably once hosted on Vercel.
Build Scripts and Configurations for React Projects
React applications typically rely on build tools like Create React App (CRA) or custom Webpack configurations to generate production-ready code. The primary goal is to create an optimized static bundle that can be served efficiently on the web. This involves configuring the build scripts in the package.json file, usually with commands such as npm run build or yarn build, which invoke the build process tailored for production.
Key configurations include specifying environment variables for different deployment environments, setting the homepage property in package.json to ensure correct URL paths, and customizing build options to include features like source maps or code splitting. For example, React’s build process automatically minifies and optimizes JavaScript and CSS assets, reducing load times and bandwidth usage.
Ensuring that the build process produces a clean, optimized output is fundamental for a successful deployment to Vercel or any hosting platform.
Best Practices for Optimizing React Applications Before Deployment
Optimizing React apps prior to deployment involves several strategies aimed at improving load times, responsiveness, and maintainability. Implementing these best practices can significantly enhance user experience and reduce hosting costs.
- Code Splitting: Divide your codebase into smaller chunks that are loaded on demand. This reduces initial load time and improves performance, especially for large applications. React’s built-in
React.lazyandSuspenseenable dynamic import of components. - Environment Setup: Use environment variables to manage different configurations for development, staging, and production environments. This approach helps in securely handling API keys and feature toggles.
- Tree Shaking: Remove unused code during the build process to minimize bundle size. Modern bundlers like Webpack automatically perform tree shaking if configured correctly.
- Optimizing Assets: Compress images, use SVGs where applicable, and leverage modern formats such as WebP to improve load times.
- Analytic and Performance Monitoring: Integrate tools like Lighthouse or WebPageTest to identify bottlenecks and ensure optimal performance metrics are met before deployment.
Adhering to these practices ensures that the React application is not only production-ready but also optimized for performance and scalability once deployed on Vercel.
Common Files and Directories Relevant to Deployment
Organizing project files and directories systematically facilitates easier deployment and maintenance. Below is a table outlining typical files and folders involved in a React project intended for deployment, their purpose, and examples.
| File Name | Purpose | Example |
|---|---|---|
package.json |
Defines project metadata, dependencies, scripts, and build commands | “name”: “my-react-app”, “scripts”: “build”: “react-scripts build” |
public/index.html |
Main HTML template that loads the React app; static assets placement | <div id=”root”></div> |
src/index.js |
Entry point for React application; renders the root component into DOM | import ReactDOM from ‘react-dom’; ReactDOM.render(<App />, document.getElementById(‘root’)); |
src/App.js |
Main application component that orchestrates other components | function App() return <div>Hello, Vercel!</div> |
build/ |
Generated folder after running the build command, containing optimized static files | Contains minified JavaScript, CSS, and static assets ready for deployment |
.env |
Environment variables for configuring the app in different environments | REACT_APP_API_URL=https://api.example.com |
README.md |
Documentation for project setup, deployment instructions, and dependencies | Provides guidance for developers and deployment teams |
Creating a Vercel Account and Linking Your Project
Establishing a Vercel account and connecting your React project is a crucial step toward deploying your application seamlessly. The process is designed to be user-friendly, providing developers with an efficient way to host their applications without incurring costs.
By creating an account and linking your project, you gain access to Vercel’s streamlined deployment infrastructure, automatic updates through Git integrations, and a range of developer-friendly features that enhance the deployment experience.
Signing Up for a Free Vercel Account and Email Verification
To begin utilizing Vercel, you need to sign up for a free account. This process involves providing basic information and verifying your email address to ensure account security and authenticity. The steps are straightforward and typically take only a few minutes.
- Navigate to the Vercel official website at https://vercel.com .
- Click on the “Sign Up” button located at the top right corner of the homepage.
- Choose your preferred sign-up method: via GitHub, GitLab, Bitbucket, or email. For most developers, connecting via a version control platform simplifies project importation later.
- If registering with email, enter your email address, create a secure password, and submit the form.
- Check your email inbox for a verification email from Vercel. Click on the verification link within the email to confirm your account.
- Once verified, you can log in to your Vercel dashboard and proceed with linking your projects.
Note: Ensuring the email verification step is completed is essential for enabling full account functionality, including project deployments and team collaborations.
Connecting a Git Repository to Vercel
Linking your Git repository is vital to facilitate continuous deployment and streamline updates to your React application. Vercel supports integration with popular platforms such as GitHub, GitLab, and Bitbucket, offering flexibility depending on your preferred version control system.
- Log into your Vercel dashboard and select “New Project” or click the “+” button to add a new deployment.
- Choose the Git provider you wish to connect: GitHub, GitLab, or Bitbucket. You will be prompted to authorize Vercel to access your repositories.
- Authorize Vercel by logging into your selected platform and granting the necessary permissions. This enables Vercel to access your repositories for deployment purposes.
- Once authorized, Vercel displays a list of your repositories. Select the React project repository you intend to deploy.
- Configure project settings such as the branch to deploy (typically “main” or “master”) and specify build commands if necessary. For React projects, Vercel automatically detects common configurations, but customization is available if needed.
- Click “Import” to finalize the connection. Vercel will initiate the deployment process based on the current state of the linked repository.
After linking your repository, Vercel continuously monitors it for changes. Each push to the designated branch automatically triggers a new deployment, ensuring your live application reflects the latest updates.
Visual Cues: During the import process, Vercel presents a step-by-step interface with progress indicators, repository previews, and configuration options. The dashboard provides real-time feedback, such as success messages once the deployment is complete and links to the live site.
Configuring deployment settings on Vercel

Configuring deployment settings on Vercel allows developers to tailor the deployment process to their application’s specific needs, ensuring optimal performance, security, and accessibility. Proper configuration not only streamlines the deployment workflow but also enhances the user experience through domain management and environment customization.
This section covers critical aspects of deployment configuration, including setting environment variables, defining build commands and output directories, and managing domain settings such as default and custom domains. These configurations are essential for maintaining consistency across deployments and ensuring your React application runs smoothly in the production environment.
Setting Environment Variables, Build Commands, and Output Directory
Environment variables are key-value pairs that provide runtime configuration data to your application without exposing sensitive information in the codebase. Setting these variables in Vercel ensures your React app has access to necessary API keys, feature flags, or environment-specific configurations.
- Environment Variables: These can be added via the Vercel dashboard under the project settings. For example, setting a variable like
REACT_APP_API_URLallows your React app to dynamically reference different API endpoints depending on the deployment environment. - Build Commands: Specify custom build scripts if your project requires specific steps to compile or prepare assets before deployment. For React apps created with Create React App, the default build command is typically
npm run buildoryarn build. - Output Directory: Define the folder where the build process places the static files to be served. For React applications built with Create React App, this is usually
build. Ensuring this is correctly specified guarantees that Vercel serves the most recent build artifacts.
Example: In the Vercel dashboard, set
Build Commandtonpm run buildandOutput Directorytobuildfor a standard React project.
Customizing Domain Settings: Default and Custom Domains
Domain management is vital for branding and accessibility. Vercel provides straightforward options to set up default domains provided by Vercel or to configure custom domains for a professional appearance. Proper domain configuration improves user trust and makes it easier for visitors to access your application.
- Default Domains: When deploying a project, Vercel automatically assigns a default
your-project.vercel.appdomain, which is suitable for testing and staging purposes. - Custom Domains: To establish a custom domain, such as
www.yourwebsite.com, you must add the domain in the Vercel dashboard, verify ownership, and update DNS records with your domain registrar. Vercel provides clear guidance on DNS configuration to ensure seamless integration. - SSL/TLS Certificates: Vercel automatically provisions SSL certificates for both default and custom domains, ensuring secure HTTPS connections without additional configuration.
Deployment Configuration Options Table
The following table summarizes various deployment configuration options, their descriptions, and typical examples to assist in setting up your React application on Vercel:
| Configuration Option | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Environment Variables | Key-value pairs accessible during build and runtime to customize app behavior securely. | REACT_APP_API_URL=https://api.example.com |
| Build Command | Custom command to compile or prepare your application before deployment. | npm run build or yarn build |
| Output Directory | Folder containing static files to be served after build completion. | build |
| Default Domain | Automatically assigned Vercel subdomain for your project. | your-project.vercel.app |
| Custom Domain | Custom URL mapped to your deployment for branding and easier access. | www.yourwebsite.com |
| SSL/TLS Settings | Security certificates for encrypted connections, managed automatically by Vercel. | Enabled for all domains, no manual action required. |
Deploying the React Application for the First Time
Deploying your React application for the first time on Vercel marks an exciting milestone, transforming your local development into a live, accessible web application. This process involves a series of well-defined steps that ensure your project is correctly built, uploaded, and made available to users around the globe. Proper initial deployment also sets the foundation for seamless future updates and maintenance.This section will guide you through the detailed procedures to trigger your initial deployment, monitor its progress, troubleshoot common issues, and perform manual redeployments after making updates to your project.
By following these steps, you can ensure a smooth transition from local development to a live, functioning React site on Vercel.
Triggering the Initial Deployment
The initial deployment process on Vercel can be straightforward if you follow a structured approach. It begins with preparing your project and ends with confirming your application is live.
- Finalize Your React Project: Ensure your React application is fully functional locally. Run the build command (`npm run build` or `yarn build`) to generate an optimized production build. Verify that the build folder contains all necessary static files and that the app runs correctly locally using a static server or local preview.
- Push Your Code to Your Version Control System: Push your latest code to your Git repository (GitHub, GitLab, or Bitbucket). Ensure your main branch (commonly ‘main’ or ‘master’) has the latest stable version of your project.
- Connect Your Repository to Vercel: In the Vercel dashboard, initiate a new project and connect your Git repository if you haven’t already. Vercel automatically detects your React project and suggests build settings.
- Configure Build Settings (if needed): Confirm that the build command is set to `npm run build` and the output directory is `build`. These are typically auto-detected but can be adjusted in the project settings.
- Trigger Deployment: Once connected and configured, Vercel automatically triggers the first deployment upon the initial push to the linked branch. You can also manually trigger a deployment by clicking on the “Deploy” button within the Vercel dashboard for your project after making any subsequent pushes.
Monitoring Deployment Status and Troubleshooting
Monitoring the deployment process helps identify and resolve potential issues early, ensuring your application goes live smoothly.
During deployment, Vercel provides real-time logs that detail each step of the build and deployment process. These logs are accessible via the Vercel dashboard, where you can observe the build status and identify any errors or warnings that occur.
- Check Deployment Status: After triggering deployment, navigate to the Vercel dashboard and open your project. The status indicator will show “Building,” “Deploying,” or “Completed.” If the status remains stuck or shows an error, review the logs for specific issues.
- Identify Common Issues: Typical problems include build failures due to missing dependencies, misconfigured environment variables, or build command errors. For instance, if the build command fails because of missing polyfills, ensure all necessary dependencies are included in `package.json`.
- Resolve Errors: Address errors directly in your code or configuration. After fixing issues locally, commit and push the changes; Vercel will automatically trigger a new deployment. For environment variable issues, verify that all required variables are correctly set in the project settings.
- Using Logs for Troubleshooting: Access the detailed logs from the Vercel dashboard to understand the root cause of issues. Logs provide line-by-line feedback from the build process, allowing precise localisation of errors.
Manual Redeployment After Updates
Once your application is live, updating it is a routine task that involves committing new code and triggering redeployment to reflect changes.
Vercel simplifies this process through integration with your version control system, automatically deploying new commits. However, manual redeployment may sometimes be necessary, especially when deploying non-code updates or fixing deployment issues.
- Push Changes to Your Repository: Make updates to your React project locally, then commit and push these changes to your main branch or the branch linked to Vercel.
- Automatic Deployment: Vercel detects the new push and begins a new deployment automatically. You can monitor the progress through the dashboard.
- Manual Redeployment via Vercel Dashboard: If automatic deployment is disabled or you want to redeploy without new commits, navigate to the project dashboard, click the “Deployments” tab, and select the “Redeploy” button associated with the latest deployment or a specific previous deployment. This action triggers a fresh deployment of your current codebase.
Ensuring your deployment process is efficient and error-free is crucial for maintaining a reliable live application. Regularly monitor deployment logs and keep your codebase clean and well-maintained for optimal results.
Testing and verifying the deployed React application
Ensuring that a React application functions correctly after deployment is a vital step in delivering a seamless user experience. Once your application is live on Vercel, thorough testing across various browsers and devices helps identify potential issues that might not surface during local development. This process guarantees that users encounter consistent performance, appearance, and functionality regardless of their chosen platform.Verifying the deployment involves multiple layers of testing, including visual inspection, functionality checks, responsiveness validation, and performance assessment.
These steps help catch bugs, layout discrepancies, or slow load times that could impact user engagement and satisfaction. Proper testing not only confirms that your application works as intended but also optimizes its overall quality before wider user adoption.
Cross-Browser and Cross-Device Testing
Testing the React application across different browsers—such as Chrome, Firefox, Safari, Edge—and various devices—including desktops, tablets, and smartphones—ensures broad compatibility. Each browser and device may render CSS styles, handle JavaScript differently, or impose unique constraints that could affect the application’s appearance and behavior.To efficiently perform this, developers can use browser developer tools, dedicated testing platforms, or emulators. Modern browsers include device mode features that simulate different screen sizes and resolutions, enabling quick testing without needing physical devices.
For comprehensive testing, services like BrowserStack or Sauce Labs provide access to multiple browser and device configurations, allowing for more extensive verification.
Debugging Deployment Issues with Vercel Logs and Browser DevTools
When encountering issues post-deployment, Vercel logs are invaluable for diagnosing problems. The logs display server-side errors, build failures, or runtime exceptions that might have occurred during deployment or execution. Accessing these logs involves navigating to your project dashboard on Vercel and reviewing recent deployment records.Additionally, browser developer tools are essential for client-side debugging. They enable inspection of HTML elements, CSS styles, JavaScript console output, network requests, and performance metrics.
Common issues such as missing assets, JavaScript errors, or slow-loading resources can be identified and resolved by systematically analyzing these tools. For example, if images do not load correctly, checking the network tab for failed requests can reveal path or permission issues.
Verification Checklist for Deployed React Applications
A structured approach to verifying your deployed React app ensures comprehensive coverage of critical aspects. Below is a detailed checklist for methodical testing:
Visual Inspection
Confirm that the user interface matches the design specifications across browsers and devices.
Responsiveness
Test layout adjustments on different screen sizes to verify responsiveness.
Functionality
Interact with all features, forms, links, and interactive components to ensure they respond correctly.
Performance
Measure initial load times and overall responsiveness using browser performance tools.
Accessibility
Check for compliance with accessibility standards such as screen reader support and keyboard navigation.
Error Handling
Validate that error messages appear appropriately and that the app handles edge cases gracefully.
Security Checks
Ensure that sensitive data is protected and that no security vulnerabilities are evident.
Network Requests
Review all API calls and asset loads to verify successful data exchange and resource availability.
Browser Compatibility
Test across multiple browsers to detect rendering issues or script failures.
Device Compatibility
Use real devices or emulators to verify mobile responsiveness and touch interactions.
Utilizing this checklist helps identify and address potential issues proactively, resulting in a reliable and user-friendly React application. Regular testing and verification are key to maintaining high standards and ensuring your deployment on Vercel delivers a smooth, engaging experience for all users.
Managing updates and continuous deployment
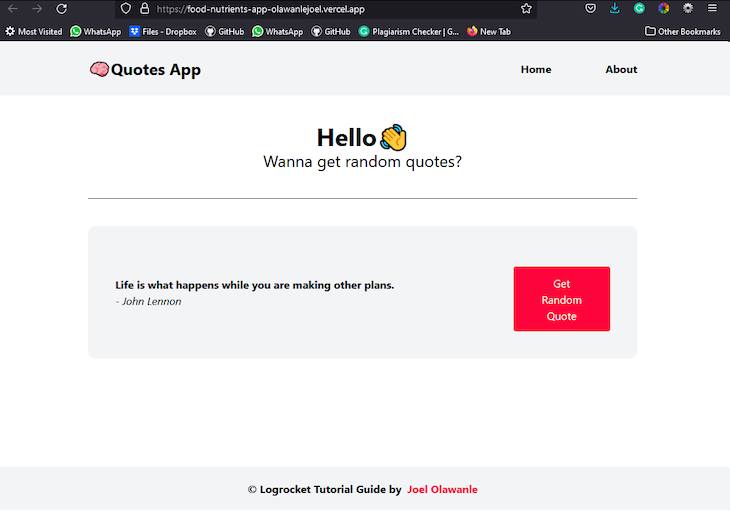
Efficient management of updates is crucial to maintaining a seamless user experience and ensuring your React application remains current. Leveraging continuous deployment practices allows developers to automate the process of deploying new changes, thereby reducing manual effort and minimizing deployment errors. Proper handling of environment variables and build settings further enhances the stability and flexibility of ongoing projects, supporting smooth and reliable updates over time.Managing updates in a React project deployed on Vercel involves integrating version control workflows, primarily through Git.
By pushing changes to your repository, Vercel automatically detects these updates and triggers a redeployment process. This automation ensures that your live application consistently reflects the latest codebase without manual intervention, fostering a DevOps culture of rapid iteration and deployment.A robust strategy involves establishing clear version control practices. Committing small, incremental changes with descriptive messages facilitates easier tracking and debugging.
Utilizing branches, such as feature branches or development branches, allows teams to test updates in isolated environments before merging into production. This method reduces the risk of introducing bugs or breaking features during deployment.To manage environment variables and build settings effectively, it is essential to keep sensitive data secure and configuration flexible. In Vercel, environment variables can be set directly within the project settings, enabling different configurations for development, preview, and production environments.
This separation ensures that API keys or secret tokens are not hardcoded in the codebase, enhancing security. When updating environment variables, a redeployment is typically required to apply changes; Vercel handles this seamlessly by triggering an automatic build upon variable updates.Strategies for maintaining stable deployment pipelines include version pinning dependencies to specific versions to prevent unexpected conflicts, and utilizing continuous integration tools alongside Vercel to automate testing before deployment.
For example, integrating GitHub Actions or CircleCI allows for running tests and linting scripts on each push, ensuring that only validated changes reach production.
“Consistent version control and environment management practices are fundamental to achieving reliable, smooth deployments and ongoing project stability in a dynamic development environment.”
Custom domains and SSL configuration
Enhancing your React application’s professionalism and security involves setting up a custom domain and enabling SSL certificates on Vercel. These steps not only improve user trust but also optimize your site’s search engine ranking. Proper configuration ensures seamless access and secure data transmission, making your application reliable and user-friendly.
Vercel simplifies the process of associating a custom domain with your deployment and automatically manages SSL certificates, providing HTTPS support. Understanding the steps involved ensures smooth setup and maintenance of your web presence with optimal security standards.
Adding custom domains to a Vercel project
Linking a custom domain to your React application hosted on Vercel requires validation and proper DNS configuration. This process verifies your ownership and directs traffic from your domain to your Vercel deployment, enabling visitors to access your site through your preferred URL.
- Access your Vercel dashboard and select the project to which you want to add a custom domain.
- Navigate to the “Settings” tab within your project dashboard.
- Click on “Domains” in the sidebar, then choose “Add Domain”.
- Enter your custom domain name (e.g., www.yourdomain.com) and click “Add”.
- Vercel will prompt you with DNS record details, typically CNAME or A records, required for domain verification.
- Login to your domain registrar’s control panel and update DNS records accordingly, matching the provided values.
- Once DNS changes propagate (which may take up to 48 hours), Vercel automatically verifies the domain and links it to your project.
During this process, ensure your DNS settings are correctly configured to avoid verification issues, and consult your domain provider’s documentation for precise instructions on updating DNS entries.
Enabling SSL certificates for secure HTTPS connections
Securing your custom domain with SSL certificates is critical for protecting data and establishing trust with your users. Vercel offers automated SSL certificate provisioning, simplifying secure setup without manual intervention.
- After your custom domain is successfully linked to your project, Vercel automatically attempts to provision an SSL certificate for your domain.
- Navigate to the “Domains” section in your project settings to monitor the SSL status.
- If the SSL certificate is pending, Vercel performs background validation and certificate issuance, which may take a few hours.
- Once active, the “SSL” status will confirm “Active” and your website will be accessible via HTTPS.
- For custom domains with DNS provider restrictions, ensure that CAA records do not interfere with SSL issuance, and update them if necessary.
Ensuring SSL certificate activation is crucial for secure data transmission, trustworthiness, and compliance with security standards such as GDPR and PCI DSS.
Default domain setup versus custom domain setup procedures
Understanding the differences between Vercel’s default domain setup and custom domain integration helps in planning your deployment process more effectively. Below is a comparative overview of both procedures:
| Feature | Default Domain Setup | Custom Domain Setup |
|---|---|---|
| Domain assignment | Automatically assigned by Vercel, typically as yourprojectname.vercel.app | Requires manual addition and DNS configuration for your own domain |
| DNS configuration | Not applicable; no DNS setup needed | Must update DNS records (CNAME, A) according to Vercel instructions |
| SSL configuration | Automatically enabled and managed by Vercel with default domain | Automatically enabled after domain verification; may require validation |
| Branding and credibility | Less professional; suitable for testing or internal projects | Enhanced branding and trust with a custom domain |
| Flexibility | Limited to Vercel subdomains | Full control over branding with your own domain |
Implementing a custom domain involves additional steps but significantly improves your application’s branding, trustworthiness, and performance. Vercel’s efficient SSL management ensures security is maintained throughout the process with minimal manual effort.
Cost considerations and limitations of the free tier
Deploying React applications to Vercel using the free plan offers an accessible and budget-friendly solution, especially for developers, startups, and hobby projects. However, it is essential to understand the scope, restrictions, and best practices associated with the free tier to ensure optimal performance without unexpected disruptions or costs. Recognizing these factors helps in planning scalable and efficient deployment strategies within the constraints of the free plan.Vercel’s free plan provides a feature-rich environment tailored for individual developers and small-scale projects.
It includes automatic deployments, serverless functions, and a global Content Delivery Network (CDN), making it an attractive platform for React app deployment. Nevertheless, the plan enforces certain usage limits designed to prevent abuse and ensure fair resource distribution among users. Being aware of these restrictions allows developers to manage their applications effectively and avoid service interruptions or unexpected charges.
Features available in Vercel’s free plan for React deployment
The free tier of Vercel supports a comprehensive set of features that facilitate the deployment of React applications with minimal setup and maintenance efforts. These features include:
- Automatic Build & Deployment: Seamless integration with GitHub, GitLab, or Bitbucket repositories allows for automatic deployment of updates.
- Global CDN: Ensures fast loading times worldwide through automatic caching and distribution of static assets.
- Serverless Functions: Enables backend functionalities without managing servers, suitable for API routes in React apps.
- Custom Domains & SSL: Supports adding custom domains with free SSL certificates for secure connections.
- Preview Deployments: Facilitates preview environments for pull requests and collaborative reviews.
These features collectively support robust React app deployment while maintaining ease of use and cost efficiency.
Usage limits and bandwidth caps
Vercel’s free tier imposes specific usage limits that are vital for users to monitor to prevent deployment issues. These limits are designed to balance resource sharing across all free users and include:
Builds per month: Up to 100 builds
Build execution time: 45 seconds per build, which can be extended by optimizing build scripts
Serverless function execution: 125,000 invocations per month with a 10-second timeout
The bandwidth limit for free accounts is set at 1 GB per month, covering all static assets, images, and responses served through the CDN. Exceeding this cap results in degraded performance or temporary suspension until the usage resets in the next billing cycle.Real-world usage scenarios demonstrate that small to medium React projects, including personal portfolios or small business websites, typically remain within these constraints.
However, high-traffic applications, large media files, or frequent updates can rapidly approach or surpass these limits, triggering the need for an upgrade.
Upgrade triggers and resource management strategies
When usage exceeds free tier boundaries, Vercel may automatically restrict deployment capabilities or bandwidth delivery until the quota resets. To avoid service interruptions, developers should proactively monitor their usage metrics via the Vercel dashboard and employ optimization techniques.Effective strategies include:
- Compressing images and static assets to reduce bandwidth consumption
- Implementing code-splitting and lazy loading to decrease build size and improve load times
- Limiting deployment frequency by batching updates or optimizing build scripts for efficiency
- Utilizing external CDNs or third-party services for large media content
In cases where project growth necessitates higher resource allocations, Vercel offers paid plans with increased limits and additional features, making it a scalable solution for expanding applications.
Last Recap
By following these steps, you can effortlessly deploy your React applications on Vercel’s free platform, enjoy reliable hosting, and focus on developing your project. Proper management of deployment settings and updates ensures your app remains secure and performs optimally over time.