Deploying a React application on Azure Cloud Hosting offers a robust and scalable solution for developers seeking reliable web performance. This comprehensive guide walks you through each essential step, from preparing your application to configuring Azure resources, ensuring a smooth deployment process. Whether you’re new to cloud hosting or looking to optimize your existing setup, understanding how to effectively deploy on Azure can significantly enhance your project’s accessibility and efficiency.
This tutorial covers key aspects such as setting up Azure services, building optimized production versions of your React app, connecting your repositories for continuous deployment, securing your application with custom domains and SSL, and monitoring your deployment for ongoing improvements. With clear instructions and best practices, you’ll be equipped to deploy your React application confidently and maintain it seamlessly on Azure cloud platform.
Introduction to deploying React apps on Azure Cloud
Hosting React applications on cloud platforms has become an essential aspect of modern web development, offering scalability, reliability, and ease of management. Microsoft Azure provides a comprehensive cloud environment that simplifies the deployment process for React apps, enabling developers to focus on creating engaging user experiences without worrying about underlying infrastructure complexities.
Azure’s cloud platform supports various deployment strategies, from simple static hosting to complex containerized applications, making it suitable for projects of all sizes. Leveraging Azure for React app deployment ensures high availability, seamless updates, and integration with other Azure services such as databases, authentication, and analytics, which can enhance the overall functionality of your application.
Benefits of Hosting React Applications on Azure Cloud Platforms
Hosting React applications on Azure offers numerous advantages that contribute to efficient and scalable web solutions:
- Scalability and Performance: Azure automatically scales resources based on traffic demands, ensuring your React app remains responsive during peak usage.
- Global Reach: With data centers worldwide, Azure enables deployment closer to your users, reducing latency and improving load times.
- Integrated Services: Azure provides seamless integration with services like Azure App Service, Azure Functions, and Azure CDN, simplifying deployment and delivery pipelines.
- Security and Compliance: Built-in security features and compliance certifications help protect your application and user data.
- Cost Management: Azure offers flexible pricing models, allowing you to optimize costs based on resource consumption and project needs.
Overview of Typical Deployment Workflows for React on Azure
Deploying React applications on Azure involves a series of steps designed to streamline updates and ensure a reliable delivery process. Typical workflows include:
- Preparing your React application by building a production-ready bundle using tools like
npm run build. - Configuring an Azure hosting environment, such as Azure App Service or Azure Static Web Apps, to serve your application.
- Deploying the build artifacts to Azure through methods like Azure CLI, GitHub Actions, or Azure DevOps pipelines.
- Configuring environment variables and custom domains as required for your application’s needs.
- Monitoring deployment status, analyzing logs, and performing post-deployment testing to verify successful setup.
Each step is critical in ensuring your React app is deployed efficiently, securely, and ready for user access. Azure’s tools and services facilitate automation and continuous deployment, making updates straightforward and minimizing downtime.
Prerequisites for Deploying React Apps on Azure
Before initiating deployment, certain prerequisites need to be in place to ensure a smooth process. These include:
- Azure Account: An active Azure subscription to access the cloud resources and services needed for deployment.
- Development Environment: Node.js and npm installed locally for building and testing your React application.
- Git Repository: Version control setup, preferably with GitHub, Azure Repos, or other repositories, to facilitate integration and continuous deployment.
- Build Configuration: Properly configured build scripts within your React project to generate optimized production files.
- Azure CLI or Azure Portal Access: Tools to create and manage Azure services, including deploying resources and configuring settings.
Ensuring these prerequisites are met helps establish a robust foundation for deploying your React app efficiently on Azure, reducing potential issues and streamlining the deployment process.
Building the React Application for Production
Preparing your React application for deployment involves configuring the build process to generate optimized, production-ready files. This step is crucial to ensure the application performs efficiently, loads quickly, and provides a seamless user experience on Azure Cloud hosting. Properly building your React app minimizes the bundle size, improves load times, and enhances overall performance, which is vital for applications serving a broad user base or handling sensitive data.
The React build process transforms your development environment into a production environment by creating static assets that are optimized for deployment. These assets include minified JavaScript, compressed CSS, and optimized images, all of which contribute to faster load times and reduced bandwidth consumption. Ensuring that the build process is correctly configured is essential for leveraging the full benefits of a cloud hosting platform like Azure.
Configuring the React Build Process for Deployment
Configuring the build process begins with setting the environment variables and build scripts in your project’s configuration files. The most common approach involves executing the command
npm run build
or
yarn build
based on your package manager. This command internally calls the React Scripts build process, which prepares your app for production.
To customize the build, modify the package.json scripts section by adjusting the build command or adding environment variables such as REACT_APP_API_URL to switch between different backend endpoints. Additionally, configuring Webpack (if ejected from Create React App) allows for more granular optimizations like code splitting, caching strategies, and plugin configurations that enhance build efficiency.
Generating Optimized Production Builds
Optimized production builds are generated by running the build command, which creates a set of static files in the build directory. These files include minified JavaScript, optimized CSS, and compressed assets, all designed to reduce load times. The build process also performs code splitting, which divides the app into smaller chunks that load on demand, improving performance for large applications.
It is essential to verify the contents of the production build folder before deployment. Files such as index.html, minified JavaScript bundles (e.g., main.[hash].js), and static assets should be present. Ensuring that all assets are correctly generated and linked prevents runtime errors post-deployment.
Differences Between Development and Production Builds
| Aspect | Development Build | Production Build |
|---|---|---|
| Code Minification | Not minified; easier to debug | Minified; optimized for performance |
| Source Maps | Included; facilitates debugging | Excluded or minimized to enhance security |
| Performance Optimization | Disabled by default; faster build speed | Enabled; reduces bundle size, improves load times |
| Debugging Tools | React Developer Tools and console logs active | React Developer Tools disabled; console logs removed |
| Build Command | npm start | npm run build |
Effective production builds prioritize performance, security, and user experience by optimizing assets and removing unnecessary debugging information.
Preparing Static Assets Before Deployment
Static assets, including images, fonts, and icons, should be optimized for fast loading and minimal bandwidth consumption prior to deployment. Compress images using tools like ImageOptim or TinyPNG to reduce file size without significant quality loss. Use modern formats such as WebP for images to achieve better compression ratios.
Organize static assets systematically within your project’s public directory, adhering to best practices for naming conventions and folder structures. This organization facilitates efficient asset management and cache control. Additionally, implement cache busting techniques by appending hashes to filenames, ensuring browsers load the latest versions of assets after updates.
Review and update references to static assets within your HTML and CSS files to reflect any filename changes due to hashing. Use tools like Webpack or other build tools to automate these updates, ensuring consistency between your codebase and deployed assets. Proper preparation of static assets significantly enhances the loading performance of your React application on Azure Cloud hosting.
Deploying React App to Azure App Service
Deploying a React application to Azure App Service offers a scalable, secure, and managed environment for hosting your frontend projects. This process allows developers to seamlessly publish updates, benefit from Azure’s integrated services, and ensure high availability for users around the globe. Whether you prefer command-line interfaces, continuous integration pipelines, or manual deployments, Azure provides versatile options tailored to your workflow.
In this section, we will explore step-by-step methods to deploy your React app using Azure CLI, connect your local Git repository for automated updates, and leverage ZIP deployment or FTP for manual upload scenarios. Understanding these deployment techniques empowers you to choose the most efficient method suited to your project requirements and team workflows.
Deploying React App via Azure CLI
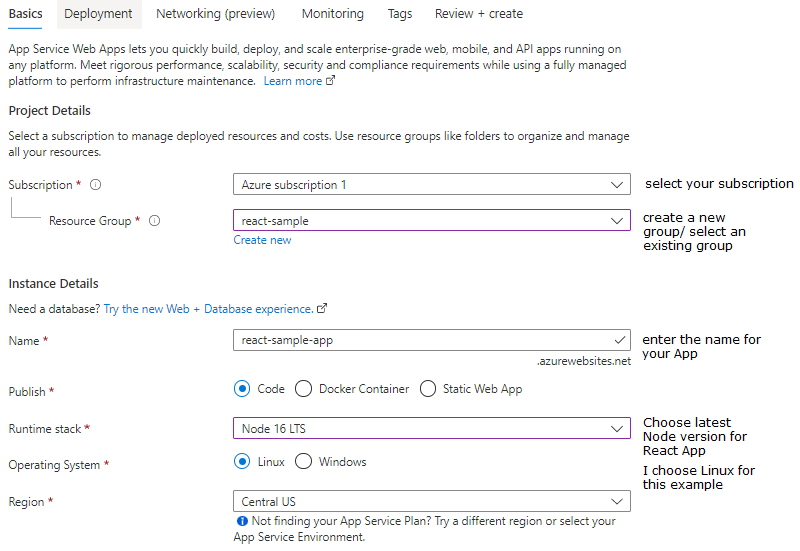
The Azure Command-Line Interface (CLI) offers a straightforward and scriptable way to deploy your React application to Azure App Service. This method is particularly useful for automation, CI/CD pipelines, and developers comfortable working from the terminal. The process involves creating an Azure resource group, setting up an App Service, and deploying your build artifacts directly from your local environment.
- Ensure Azure CLI is installed and logged in by running
az login. - Create a resource group to organize your resources:
- Create an App Service plan that defines the hosting environment:
- Create a Web App instance, specifying Node.js as the runtime if needed (for static React apps, you can use a simple web server):
- Build your React app for production locally using:
- Deploy your build directory to Azure using the Azure CLI via ZIP deployment:
- Initialize your Git repository if not already done:
- Configure your remote Azure repository using the deployment credentials provided in the Azure portal or via CLI. You can set up deployment via local Git by creating a deployment user:
- Add the Azure remote repository to your local Git configuration:
- Push your code to trigger deployment:
- ZIP Deployment: Create a ZIP archive of your production build and upload it via Azure CLI or Azure Portal:
- FTP Deployment: Configure FTP credentials in the Azure portal, then use an FTP client to upload your build files into the site’s /site/wwwroot directory. FTP provides a visual interface for manual uploads, suitable for quick patches or small updates.
- Azure CLI ZIP Deployment: Ideal for scripting and automation, supports quick uploads, and integrates seamlessly into CI/CD pipelines.
- Local Git Deployment: Facilitates continuous deployment, version control, and collaborative development; instantly reflects updates upon push.
- FTP Deployment: Provides a simple, manual upload mechanism; suitable for quick patches or legacy systems without Git integration.
- Azure DevOps Pipelines: Enables comprehensive CI/CD workflows with automated testing, building, and deployment, ensuring high-quality releases.
- Container Deployment (Azure Container Instances or Kubernetes): Suitable for complex applications requiring containerization, scalability, and orchestration capabilities.
- Navigate to your specific Azure App Service or Static Web App instance in the Azure portal.
- Select the “Configuration” option from the left-hand menu.
- Within the “Application settings” tab, click on the “New application setting” button.
- Enter the name of the environment variable in the “Name” field, and the corresponding value in the “Value” field.
- Optionally, toggle the “Deployment slot setting” if you want this setting to be slot-specific.
- Click “OK” to save each setting, then click “Save” at the top of the Configuration page to apply changes.
- Create an Azure Key Vault instance in your Azure portal.
- Add secrets such as API keys or connection strings to the Key Vault.
- Assign appropriate access policies to your App Service or Static Web App to allow access to the Key Vault.
- In your application’s code, access these secrets via environment variables that reference the Key Vault, or configure your app to retrieve secrets directly during startup.
- Access the “Configuration” section of your Azure App Service or Static Web App as described earlier.
- Modify existing environment variables or add new ones directly within the portal interface.
- Click “Save” to apply the changes. Azure automatically updates the environment variables for the running instance, often with minimal or no downtime.
- For certain cases, a restart of the app might be necessary to fully apply the new settings, which can be done via the “Restart” button in the overview section.
- Access the Azure Portal and navigate to your specific App Service or Static Web App instance.
- Select the “Custom domains” section from the left-hand menu.
- Click on “Add custom domain” and enter your desired domain name.
- Verify domain ownership by creating specific DNS records, typically a CNAME or TXT record, at your domain registrar.
- Azure will validate the DNS records. Once validated, confirm the addition of the custom domain.
- Configure DNS settings at your domain registrar to point your domain to Azure’s endpoints, ensuring proper resolution and traffic routing.
- Navigate to the “Custom domains” section of your Azure App Service or Static Web App.
- Select your custom domain that requires SSL.
- Click on “Add TLS/SSL Binding” or similar options available within your deployment portal.
- Choose the SSL certificate type:
- App Service Managed Certificate (free, automatically renewed)
- Bring Your Own Certificate (BYOC) from a third-party certificate authority, requiring manual upload and renewal management
- If using a free App Service Managed Certificate, select the certificate and bind it to your custom domain.
- For third-party certificates, upload the certificate files, configure the binding, and ensure the domain is correctly associated.
- Verify the SSL setup by accessing your domain via https:// and checking for secure padlock indicators in browsers.
- Configure HTTP to HTTPS redirection to ensure all traffic uses encrypted channels, typically by setting rules within your web app or via Azure Portal settings.
- Create DNS TXT or CNAME records at your domain registrar as instructed by Azure.
- Wait for DNS propagation and verify records within Azure portal.
- Ensure the domain points correctly to Azure endpoints.
- Select the appropriate SSL certificate type (Managed or third-party).
- Bind the certificate to your custom domain in Azure portal.
- Implement HTTP to HTTPS redirection.
- Enforce HTTPS on all pages.
- Utilize Azure Security Center for monitoring vulnerabilities.
- Configure Web Application Firewall (WAF) if applicable.
- Regularly update your application dependencies and Azure configurations.
- Azure Monitor: Provides comprehensive telemetry data including application metrics, logs, and alerts. You can set up custom dashboards to visualize real-time performance metrics such as response times, error rates, and server CPU/memory utilization.
- Azure Application Insights: Offers deep application performance monitoring, including request rates, dependency tracking, failures, and exception diagnostics. It integrates seamlessly with React applications to provide user-centric insights and performance data.
- Azure Portal Uptime Monitoring: The portal includes availability tests like ping tests and HTTP checks that can be scheduled at regular intervals to verify application accessibility from various geographic locations.
- Verify deployment logs: Check the deployment output logs for error messages or warnings. In Azure App Service, navigate to the Deployment Center and examine the logs for build failures or deployment pipeline issues.
- Check environment variables and settings: Ensure all necessary environment variables are correctly set in Azure portal under Application Settings. Misconfigured variables often lead to runtime errors.
- Validate build configurations: Confirm that the production build of the React app was correctly generated using ‘npm run build’ and that all build artifacts were properly uploaded.
- Inspect network and permissions: Verify CORS policies, firewall rules, and permissions that might block API calls or static asset loading.
- Review application logs: Use Azure Diagnostics and Application Insights to examine logs for runtime errors, unhandled exceptions, or failed dependencies.
- Accessing logs: Navigate to your App Service or Static Web Apps resource, then select the ‘Logs’ section. For App Service, enable Application Logging (Filesystem or Blob) to capture detailed runtime information.
- Utilizing Log Stream: The Log Stream feature allows real-time viewing of logs, enabling immediate detection of errors during application startup or runtime.
- Using Application Insights: Configure Application Insights to automatically collect request, dependency, exception, and custom event logs. On the Azure portal, access the ‘Application Insights’ resource linked to your app for detailed diagnostics.
- Enabling diagnostic settings: Set up diagnostic settings to export logs to Azure Storage, Event Hubs, or Log Analytics for long-term analysis and alerting.
- Interpreting logs: Regularly analyze logs for recurring errors or performance bottlenecks, paying special attention to unhandled exceptions and dependency failures.
- Preparing the updated React build: Run `npm run build` or `yarn build` locally to generate the latest production-ready files.
- Testing the build locally or in a staging environment to verify changes and ensure stability.
- Uploading or deploying the new build to Azure: This could involve replacing files directly in Azure App Service or updating the static web app repository.
- Restarting the Azure service if necessary to apply updates, ensuring minimal service disruption.
- Verifying deployment success by checking application functionality and performance on the live environment.
- Utilizing version control systems like Git to track all changes, facilitating easy rollback to previous stable states.
- Implementing feature branches and tags to distinguish release versions clearly.
- Maintaining a backup of previous production builds before deploying updates, enabling quick restoration if needed.
- Using Azure Deployment Slots to deploy updates to a staging environment first, then swapping to production after validation, which allows quick rollback if issues arise.
- Defining release cycles aligned with business needs, such as weekly, bi-weekly, or monthly updates.
- Implementing a continuous integration/continuous deployment (CI/CD) pipeline to automate testing and deployment processes.
- Scheduling maintenance windows during low-traffic periods to minimize user impact.
- Monitoring deployment outcomes and collecting user feedback to inform future updates.
- Azure DevOps Pipelines: Provides end-to-end CI/CD workflows for React applications, integrating build, test, and deployment stages.
- GitHub Actions: Automates deployment processes directly from GitHub repositories, supporting custom workflows for React apps.
- Jenkins: Configurable automation server capable of orchestrating complex deployment pipelines with scripting support.
- Azure CLI Scripts: Command-line scripts for automating deployment tasks such as file uploads, resource management, and environment setup.
- PowerShell Scripts: Useful for automating repetitive deployment steps, especially in Windows-based environments.
az group create --name MyResourceGroup --location "East US"
az appservice plan create --name MyPlan --resource-group MyResourceGroup --sku B1 --is-linux
az webapp create --resource-group MyResourceGroup --plan MyPlan --name MyReactApp --runtime "NODE|14-lts"
npm run build
az webapp deployment source config-zip --resource-group MyResourceGroup --name MyReactApp --src ./build.zip
Replace build.zip with the zipped version of your build directory. This method ensures fast and reliable deployment, especially suited for automated scripts.
Connecting Local Git Repository for Continuous Deployment
Linking your local Git repository with Azure App Service facilitates continuous deployment, allowing automatic updates whenever code is pushed to the configured branch. This method streamlines the development workflow and minimizes manual upload efforts.
git init
az webapp deployment user set --user-name--password
git remote add azure
The deployment URL typically follows this pattern: https://.
git push azure main
Azure will automatically build and deploy your React application, keeping your website up-to-date with the latest commits. This is highly effective for collaborative teams and projects under active development.
Deployment Using ZIP Deployment or FTP
Manual deployment methods like ZIP deployment or FTP are beneficial when quick updates are needed or when integrating with existing workflows that do not rely on Git. These approaches provide flexibility for deploying pre-built assets or integrating with third-party deployment tools.
az webapp deployment source config-zip --resource-group MyResourceGroup --name MyReactApp --src ./build.zip
While ZIP and FTP deployments are straightforward, they lack the automation and version control benefits of Git-based deployment. They are optimal for occasional updates or scenarios where integrating with CI/CD pipelines isn’t feasible.
Deployment Options with Their Advantages
Several deployment methods are available for hosting your React app on Azure, each with specific advantages tailored to different workflows and project needs:
Choosing the appropriate deployment option depends on project scale, team workflows, and automation requirements. Combining methods can also optimize deployment efficiency and reliability.
Deploying React app to Azure Static Web Apps
Azure Static Web Apps offers a streamlined and efficient hosting solution tailored specifically for modern frontend frameworks like React. By deploying your React application on this platform, you gain access to a globally distributed CDN, simplified deployment workflows, and an integrated environment that enhances performance and scalability. This approach is especially advantageous for developers seeking rapid deployment cycles and cost-effective hosting options designed for static sites.
Leveraging Azure Static Web Apps for React projects enables automated deployment processes directly linked to your source code repositories. This integration ensures that every code commit triggers a deployment pipeline, reducing manual intervention and minimizing deployment errors. It also supports custom domains, SSL certificates, and seamless integration with APIs and backend services, creating a comprehensive full-stack solution with minimal configuration overhead.
Linking a GitHub Repository for Automated Deployments
Establishing a connection between your GitHub repository and Azure Static Web Apps is fundamental for enabling continuous deployment. This setup automates the deployment process, ensuring that your React app is always up-to-date with the latest code changes without manual intervention. The process involves granting Azure permissions to access your repository and configuring the workflow files to specify build and deployment commands.
The typical workflow configuration is defined in a YAML file located in the `.github/workflows/` directory of your repository. This file includes steps to check out code, install dependencies, build the React application, and deploy the static files to Azure. During setup, you specify the branch to monitor, the build commands such as `npm run build`, and the output directory, usually `build/`.
Azure handles the rest, automatically deploying your React app whenever changes are pushed to the linked branch.
Configuration Settings in Workflow Files or Deployment Scripts
Proper configuration of your workflow files is crucial for smooth deployments. A representative GitHub Actions workflow for React deployment to Azure Static Web Apps typically includes environment variables, build commands, and the deployment destination. Below is an Artikel of common settings:
name: Azure Static Web Apps CI/CD
on:
push:
branches:
-main # or your deployment branch
jobs:
build_and_deploy:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
-name: Checkout code
uses: actions/checkout@v2
-name: Set up Node.js
uses: actions/setup-node@v2
with:
node-version: '16'
-name: Install dependencies
run: npm install
-name: Build React app
run: npm run build
-name: Deploy to Azure Static Web Apps
uses: Azure/static-web-apps-deploy@v1
with:
azure_static_web_apps_api_token: $ secrets.AZURE_STATIC_WEB_APPS_API_TOKEN
repo_token: $ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN
action: "upload"
#### Specify the app location if not root
app_location: "/"
#### Output directory after build
output_location: "build"
Key parameters like `app_location` and `output_location` need adjustment based on project structure. Also, ensure that secrets such as the Azure API token are securely stored in your repository settings. This setup guarantees that deployments are automated, consistent, and aligned with your source code changes.
Responsive HTML Table Comparing App Service and Static Web Apps
Choosing between Azure App Service and Static Web Apps depends on project requirements regarding deployment complexity, cost, and scalability. The table below provides a clear comparison to assist in decision-making:
| Feature | Azure App Service | Azure Static Web Apps |
|---|---|---|
| Deployment Method | Supports deploying server-side rendered applications, backend APIs, and static content via FTP, Git, or Azure CLI. | Optimized for static sites; deployment primarily through GitHub or Azure DevOps with CI/CD workflows. |
| Cost | Higher due to resource provisioning, especially for larger or dynamic applications. Free tier available with limitations. | More cost-effective for static sites; free tier available with generous limits, pay-as-you-go for additional bandwidth and features. |
| Scalability | Auto-scaling based on resource allocation; suitable for complex backend integrations and dynamic content. | Highly scalable globally via CDN; ideal for high-traffic static content with minimal latency. |
| Use Case Suitability | Full-stack applications, backend integrations, dynamic content, server-side rendering. | Static websites, Single Page Applications, JAMstack sites, content-heavy sites with minimal backend needs. |
Configuring environment variables and app settings

Proper configuration of environment variables and app settings is crucial for deploying React applications on Azure, ensuring that sensitive information remains secure and that the application behaves correctly across different environments such as development, staging, and production. Azure provides flexible options to manage these configurations without the need for redeployment, enhancing both security and operational efficiency.
Managing environment variables securely and efficiently allows developers to separate configuration from code, making applications more portable and easier to maintain. Azure’s portal interface offers straightforward procedures to set, update, and manage these variables, supporting seamless adjustments to app behavior without interrupting service availability.
Setting environment variables in Azure portal
Azure App Service and Static Web Apps offer intuitive interfaces to define environment variables, which are then injected into the runtime environment of the application. This process ensures that sensitive data such as API keys or database connection strings are kept outside of the source code, reducing security risks. Follow these steps to configure environment variables through the Azure portal:
Secure management of app secrets
Handling secrets such as API keys, database credentials, or tokens demands careful attention to security. Azure offers several mechanisms to manage secrets securely, minimizing risks associated with exposure or accidental leaks:
Azure Key Vault is the recommended service for storing and managing secrets centrally, providing controlled access, auditing, and encrypted storage.
To integrate secrets securely:
Updating environment configurations without redeployment
Azure supports dynamic updates to environment variables and app settings, enabling adjustments without redeploying or restarting the application. This capability facilitates rapid configuration changes, bug fixes, or feature toggles, minimizing downtime and deployment overhead.
To update environment variables dynamically:
Key environment settings for React applications on Azure
When deploying React apps, certain environment variables and settings are typically configured to ensure correct runtime behavior, security, and performance. Examples include:
| Setting Name | Description | Example Value |
|---|---|---|
| NEXT_PUBLIC_API_URL | Base URL for API endpoints used by the React app. Publicly accessible for client-side code. | https://api.example.com |
| REACT_APP_FIREBASE_API_KEY | API key for Firebase services, kept secret in environment variables. | your-firebase-api-key |
| NODE_ENV | Specifies the environment mode, affecting build optimizations and error reporting. | production |
| APP_SECRET | Sensitive secrets such as tokens or keys, stored securely and not exposed in client code. | encrypted-value |
The careful configuration of these settings ensures that the React application runs securely, efficiently, and is adaptable to different deployment contexts.
Custom Domain and SSL Setup
Implementing a custom domain and securing your React application’s deployment with SSL certificates are essential steps to establish a professional, trustworthy online presence. Proper configuration not only enhances brand recognition but also ensures data security for your users, fostering confidence in your application hosted on Azure Cloud. This section details the necessary procedures to add your custom domain to Azure services and enable SSL certificates for HTTPS, thereby safeguarding your application’s communication channels.Securing your React app with a custom domain and SSL involves several coordinated steps.
Azure offers integrated tools and services to simplify domain management and certificate provisioning. Following these steps accurately guarantees a seamless and secure user experience, complying with modern web standards and best practices.
Adding Custom Domains to Azure Deployments
Custom domain integration allows you to replace default Azure URLs with your personalized domain name, such as www.example.com. This process involves domain verification and configuration within the Azure portal and your domain registrar.
To add a custom domain to your Azure Web App or Static Web App, follow these key steps:
It is crucial to ensure that DNS propagation completes, which can take from a few minutes up to 48 hours, depending on your DNS provider. Proper verification guarantees that your domain is correctly linked to your Azure deployment, providing a seamless branded experience for your users.
Enabling SSL Certificates for HTTPS
Enabling SSL certificates ensures encrypted communication between your users and the hosted application, protecting sensitive data and improving search engine rankings. Azure provides streamlined options for SSL certificate management, including free certificates through App Service Managed Certificates and integration with third-party certificate authorities.
The following steps Artikel the process of enabling SSL for your custom domain:
Note: Regularly monitor your SSL certificates for renewal and validity to prevent security warnings or service interruptions.
Domain Verification, SSL Configuration, and Security Best Practices
The following table summarizes the essential steps involved in domain verification, SSL configuration, and security best practices to ensure a robust deployment.
| Task | Steps | Best Practices |
|---|---|---|
| Domain Verification |
|
|
| SSL Certificate Configuration |
|
|
| Security Best Practices |
|
|
Monitoring and troubleshooting deployment issues
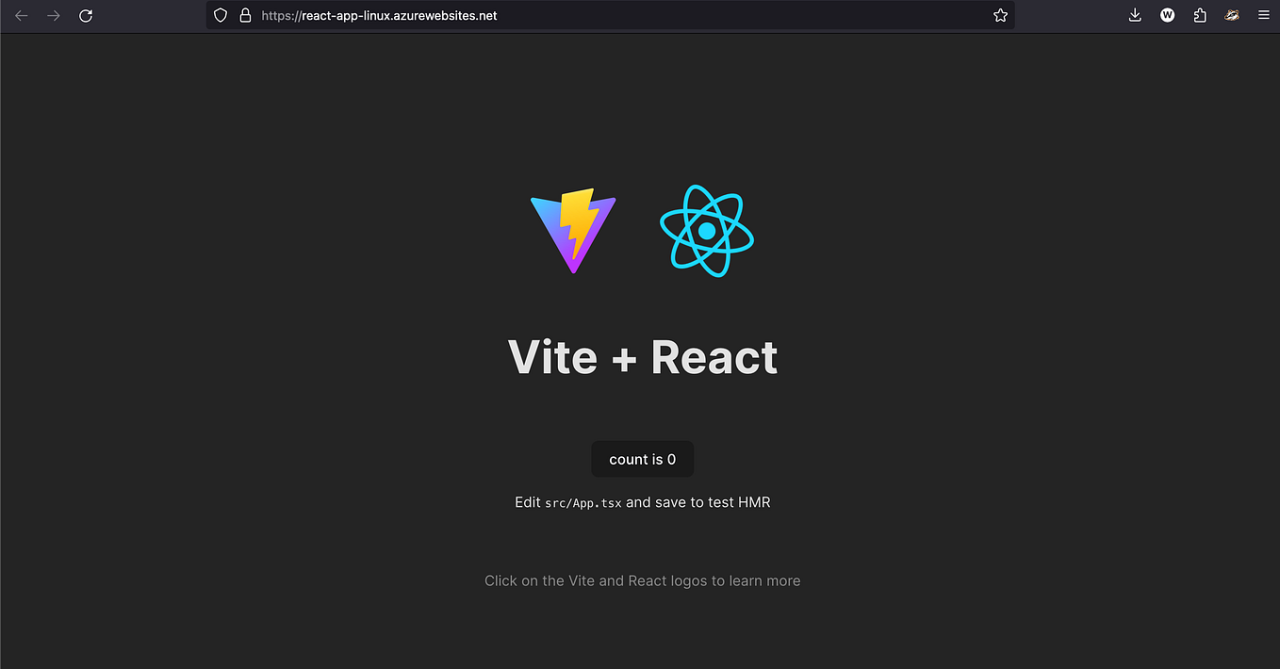
Ensuring that your React application performs optimally after deployment is vital for delivering a seamless user experience. Monitoring tools and troubleshooting strategies help identify and resolve issues promptly, minimizing downtime and maintaining the application’s reliability on Azure Cloud. This section explores effective methods to monitor app performance and troubleshoot common deployment challenges encountered during the deployment lifecycle.
Azure provides a comprehensive set of tools and features designed to assist developers and administrators in maintaining application health. By leveraging these tools, teams can proactively monitor uptime, diagnose errors, and optimize performance, ensuring that the deployed React app remains robust and user-friendly.
Monitoring app performance and uptime on Azure
Effective monitoring involves tracking key performance metrics and uptime indicators to assess the health of your deployed React application. Azure offers several integrated tools for this purpose, which can be configured to suit specific application needs.
Monitoring these metrics allows teams to quickly identify anomalies, understand usage patterns, and respond to incidents proactively. Setting up automated alerts based on thresholds ensures timely notifications for issues such as increased error rates or server downtime.
Troubleshooting steps for common deployment errors
Deployment errors can arise from various configuration issues, code incompatibilities, or environment misconfigurations. Addressing these efficiently requires a systematic approach to identify root causes and implement corrective measures.
Addressing each step methodically helps isolate issues quickly, reducing recovery time and improving deployment stability.
Reviewing logs and diagnostics in the Azure portal
Azure portal provides centralized access to logs and diagnostic tools essential for troubleshooting deployment issues. Regular review of logs helps maintain application health and diagnose problems effectively.
Consistent log review and diagnostics are fundamental to maintaining application reliability, enabling early detection and resolution of issues before they impact end-users.
Updating and maintaining deployed React applications
Maintaining React applications on Azure Cloud involves routine updates, effective version management, and proactive monitoring to ensure optimal performance and security. Regular updates help incorporate new features, fix bugs, and address security vulnerabilities, keeping the application reliable and secure for users. Establishing structured maintenance procedures ensures the application remains current and responsive to evolving business needs.Effective management of version control and rollback strategies are critical in minimizing downtime and mitigating risks during updates.
Proper planning and automation facilitate seamless deployment cycles, enabling teams to deliver continuous improvements efficiently. Leveraging automation tools and scripting enhances deployment consistency and reduces manual errors, ensuring a smooth operational workflow.
Procedures for updating React apps on Azure
Updating React applications hosted on Azure involves a series of well-defined steps to ensure smooth deployment and minimal downtime. The typical process includes:
Automated deployment pipelines can streamline this process, reducing manual intervention and enhancing deployment reliability.
Managing version control and rollbacks
Managing versions effectively is essential for maintaining application stability and enabling quick recovery from issues. Best practices include:
A well-structured version control strategy minimizes risks associated with updates and supports rapid recovery in case of unforeseen issues.
Scheduling deployment plans for continuous improvement
Establishing a deployment schedule supports consistent application enhancement and reduces disruption. The scheduling process includes:
Regular scheduled deployments foster an environment of continuous improvement, allowing teams to adapt quickly to new requirements or issues.
Examples of deployment automation tools and scripts
Automation tools and scripts streamline deployment workflows, reduce manual errors, and enhance operational efficiency. Relevant examples include:
Implementing these tools and scripts enhances deployment consistency, accelerates release cycles, and supports scalable maintenance strategies for React applications on Azure Cloud.
Closing Notes
Successfully deploying your React application on Azure Cloud Hosting not only ensures high availability and scalability but also empowers you with tools to monitor, update, and secure your app effectively. By following this guide, you’ll streamline your deployment workflow, enjoy the benefits of Azure’s robust infrastructure, and be well-prepared to handle future updates with ease. Embracing Azure for hosting your React project opens up new opportunities for growth and innovation in your web development journey.