Navigating the complexities of a WordPress website often leads to encountering PHP memory limit issues, a common hurdle that can significantly impact your site’s performance and user experience. This comprehensive guide offers a deep dive into understanding, identifying, and resolving these memory-related challenges, ensuring your WordPress site runs smoothly and efficiently.
From understanding the fundamentals of PHP memory limits and their impact on WordPress functionality to practical troubleshooting techniques and advanced optimization strategies, we’ll equip you with the knowledge and tools necessary to diagnose and resolve memory-related problems. We’ll explore how to identify memory-intensive processes, increase memory limits when necessary, and implement best practices for optimizing your website for peak performance, all presented in a clear, step-by-step format.
Understanding WordPress PHP Memory Limits
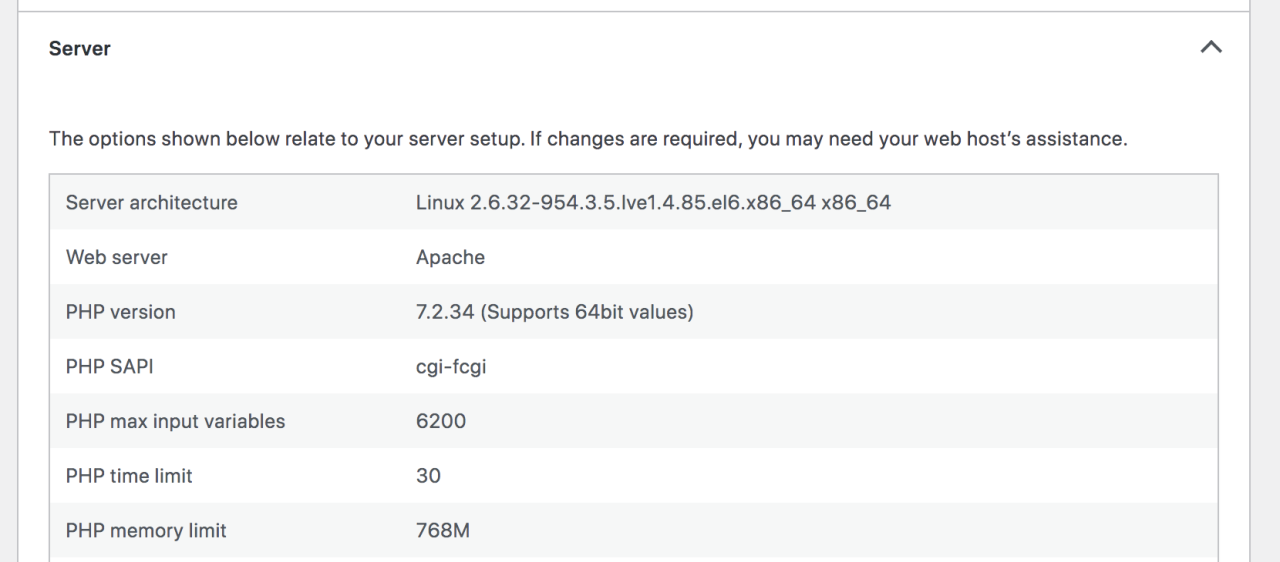
PHP memory limits are a critical aspect of WordPress performance, directly influencing how your website functions and how users experience it. Understanding these limits is essential for troubleshooting performance issues and ensuring your site runs smoothly.
The Role of PHP Memory Limits in WordPress Performance
PHP memory limits dictate the amount of memory a PHP script can consume while running on your web server. WordPress, being built on PHP, relies heavily on these limits. Insufficient memory can lead to various problems, from slow loading times to complete website crashes. Optimizing your memory settings is a key step in maintaining a healthy and efficient WordPress site.
Definition of PHP Memory Limits and Their Importance
A PHP memory limit is the maximum amount of RAM (Random Access Memory) that a PHP script is allowed to use. This limit prevents poorly written or resource-intensive scripts from consuming all of the server’s resources, potentially crashing the server and affecting other websites hosted on it. It is important to monitor and adjust this limit appropriately.
Impact of Exceeding the Memory Limit on Website Functionality and User Experience
Exceeding the PHP memory limit results in a variety of detrimental effects on your WordPress website. These can significantly degrade the user experience.
- Error Messages: The most common symptom is the display of error messages, such as “Fatal error: Allowed memory size exhausted” or “PHP Fatal error: Out of memory.” These messages directly inform the user that the script has run out of memory.
- Slow Loading Times: Even before the limit is completely reached, the website can become sluggish. Scripts may take longer to execute, resulting in slower page load times and a frustrating experience for users.
- Incomplete Tasks: Tasks like image uploads, theme installations, or plugin updates may fail to complete. This is because the scripts involved in these actions require sufficient memory to function properly.
- Website Crashes: In severe cases, exceeding the memory limit can cause the entire website to crash, making it inaccessible to visitors. This leads to lost traffic, potential revenue loss, and damage to the website’s reputation.
Default PHP Memory Limit Settings and Hosting Environment Variations
The default PHP memory limit varies depending on your hosting provider and the PHP version being used. These default values are not always sufficient for all WordPress websites, especially those using numerous plugins, complex themes, or handling large amounts of media.
- Default Values: Common default values include 32MB, 64MB, and sometimes even 128MB. Older hosting setups may still use lower default values.
- Hosting Provider Influence: Shared hosting environments often impose stricter limits to ensure fair resource allocation among users. Managed WordPress hosting providers typically set higher default limits, optimized for WordPress performance.
- PHP Version Impact: Newer PHP versions may have different default memory settings than older versions. Additionally, the memory requirements of WordPress itself and its plugins can change with updates.
- Checking Your Current Limit: You can determine your current PHP memory limit by creating a PHP file (e.g., `memory-limit.php`) with the following code and uploading it to your WordPress directory:
<?php echo 'Memory Limit: ' . ini_get('memory_limit'); ?>Then, access this file through your web browser (e.g., `yourwebsite.com/memory-limit.php`). This will display your current PHP memory limit.
Identifying Memory Limit Issues
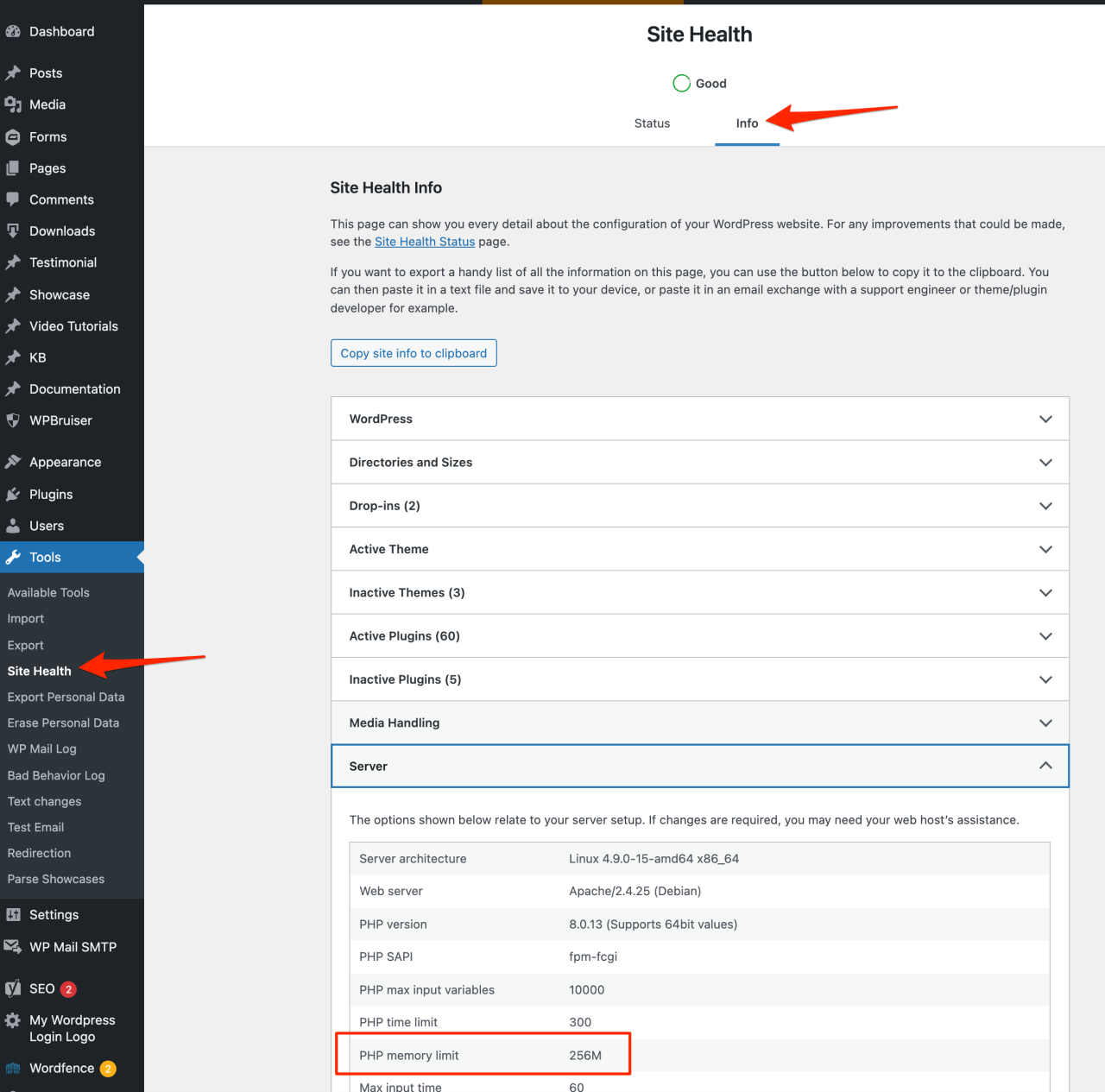
Understanding when your WordPress site is bumping up against its PHP memory limit is crucial for maintaining a smooth and efficient user experience. Recognizing the symptoms and knowing how to diagnose the problem allows you to proactively address it before it impacts your site’s performance or leads to errors. This section will guide you through the common indicators of memory limit issues, the specific error messages to watch out for, and the tools and techniques available to monitor your site’s memory consumption.
Common Symptoms of PHP Memory Limit Problems
Several telltale signs can indicate that your WordPress site is running out of PHP memory. These symptoms can manifest in various ways, affecting both the front-end and back-end operations of your website.
- White Screen of Death (WSOD): One of the most common and frustrating symptoms is the WSOD. This blank page appears when PHP encounters a fatal error, often due to memory exhaustion. The user sees nothing but a white screen, making it impossible to access the site.
- Incomplete Page Loading: Pages might load partially, with some elements missing or displaying incorrectly. This often happens when the script runs out of memory before it can fully render the page.
- Error Messages in the WordPress Dashboard: You might see error messages displayed within the WordPress dashboard itself. These errors often indicate that a plugin or theme is attempting to use more memory than is allocated.
- Problems Uploading Media: When attempting to upload large images, videos, or other media files, you might encounter errors. The server may fail to process the upload due to insufficient memory.
- Issues with Plugin Activation/Deactivation: Activating or deactivating plugins might fail, or the process might take an unusually long time. This is particularly true for plugins that are resource-intensive.
- Slow Website Performance: Even without outright errors, a website that consistently feels slow or sluggish can be a sign of memory issues. The server spends more time managing memory, which can impact response times.
Specific Error Messages Related to Memory Limits
When PHP runs out of memory, it typically generates specific error messages. Recognizing these messages is critical for pinpointing the root cause of the problem. These error messages usually appear in your browser, server logs, or within the WordPress dashboard.
- Fatal Error: Allowed memory size exhausted: This is the most common and direct error message indicating that the PHP script has exceeded the memory limit. The message will often include the file name and the line number where the error occurred.
Fatal error: Allowed memory size of 67108864 bytes exhausted (tried to allocate 786432 bytes) in /path/to/your/file.php on line 123
- Error establishing a database connection: While not always directly related to memory limits, this error can sometimes occur if the server is under heavy load, potentially due to memory exhaustion.
- Internal Server Error (500 Error): This generic error message can be caused by various issues, including memory limit problems. Check your server logs for more specific details.
- Timeout Errors: If a PHP script takes too long to execute because of memory constraints, it might trigger a timeout error. This can prevent the page from loading.
- Memory allocation errors from specific plugins: Some plugins may display custom error messages related to memory allocation if they encounter problems.
Tools and Techniques to Monitor Memory Usage
Several tools and techniques are available to monitor memory usage within your WordPress environment. Using these tools will help you understand how your website is consuming memory and identify potential bottlenecks.
- WordPress Plugins: Several plugins are designed to monitor memory usage, such as the “Memory Usage” plugin. These plugins can display real-time memory usage in the WordPress dashboard. They can also help you identify which plugins are using the most memory.
- Server-Side Monitoring Tools: Your web hosting provider may offer server-side monitoring tools, such as cPanel or Plesk. These tools can provide detailed information about server resource usage, including memory consumption, CPU usage, and disk space.
- PHP `memory_get_usage()` Function: Developers can use the PHP `memory_get_usage()` function to track memory usage within their code. This function returns the amount of memory, in bytes, that is currently being used by the PHP script.
- Server Logs: Regularly review your server’s error logs. These logs often contain valuable information about memory-related errors, including the specific file and line number where the error occurred.
- Debugging Tools: Utilize debugging tools, such as Xdebug, to profile your code and identify memory leaks or inefficient code. These tools provide detailed insights into how your code uses memory.
Checking Current Memory Usage in WordPress
There are several ways to check your current memory usage. The method you choose will depend on your technical skills and access to different tools.
- Using a WordPress Plugin: Install a plugin like “Memory Usage.” After activating the plugin, it will display the current PHP memory usage in the WordPress admin bar or a dedicated dashboard widget. This gives you a quick and easy way to monitor memory usage.
- Checking Server Logs: Access your server’s error logs (often located in your hosting control panel or via FTP). Look for error messages related to memory exhaustion. These messages often include details about the memory limit and the amount of memory being used.
- Using PHP Code (for developers): Add the following code snippet to your theme’s `functions.php` file (or a custom plugin) to display the current memory usage on a specific page. Remember to remove this code after you’ve finished monitoring.
<?php function display_memory_usage() $memory_usage = memory_get_usage(true); if ($memory_usage < 1024) $memory_usage = $memory_usage . " bytes"; elseif ($memory_usage < 1048576) $memory_usage = round($memory_usage / 1024, 2) . " KB"; else $memory_usage = round($memory_usage / 1048576, 2) . " MB"; echo "<p>Current memory usage: " . $memory_usage . "</p>"; add_action('wp_footer', 'display_memory_usage'); ?>
Locating Memory-Intensive Processes
Identifying the source of high memory consumption is crucial for resolving WordPress PHP memory limit issues. This involves pinpointing the specific plugins, themes, or other processes that are utilizing excessive memory resources. By systematically analyzing memory usage, you can identify and address the root cause, leading to improved website performance and stability.
Common Causes of High Memory Consumption in WordPress
Several factors can contribute to high memory consumption in a WordPress environment. Understanding these common culprits is essential for effective troubleshooting.
- Poorly Optimized Plugins: Plugins with inefficient code, excessive database queries, or memory leaks are significant memory consumers. These plugins might load unnecessary resources or fail to release memory after use, leading to gradual memory exhaustion. For instance, a plugin that processes large image files without proper optimization can quickly consume available memory.
- Complex Themes: Themes that incorporate extensive features, complex animations, or numerous third-party scripts can also contribute to high memory usage. The more features a theme includes, the more resources it typically requires to function. This can be particularly problematic if the theme is not well-coded or optimized.
- Large Media Libraries: Websites with extensive media libraries, especially those containing high-resolution images or videos, can strain memory resources. Each image or video file loaded by a page consumes memory.
- Database Bloat: Over time, WordPress databases can become bloated with unnecessary data, such as post revisions, spam comments, and transient options. This bloat increases the resources needed to query the database, contributing to memory consumption.
- Inefficient Code: Poorly written custom code, including functions added to the `functions.php` file or custom plugins, can lead to memory inefficiencies. Inefficient code might perform redundant operations or fail to properly manage memory allocation.
- Server Configuration: The server's PHP configuration, including the allocated memory limit, can impact memory usage. If the allocated memory is insufficient, the website will experience memory limit issues.
Identifying Memory-Intensive Plugins or Themes
Determining which plugins or themes are consuming the most memory is a critical step in resolving memory limit issues. Several tools and methods can be employed to analyze memory usage effectively.
- Using a Debugging Plugin: Plugins like Query Monitor or Debug Bar can provide real-time insights into memory usage. These plugins monitor the memory consumed by each plugin and theme, enabling you to identify the resource-intensive components. For example, Query Monitor can display the memory usage of each database query, helping pinpoint inefficient database operations.
- Analyzing Server Logs: Server error logs can provide valuable information about memory limit errors. These logs often indicate the specific plugin or theme that triggered the error, along with the memory limit that was exceeded.
- Profiling with Xdebug: Xdebug is a powerful debugging tool that can profile PHP code execution, revealing the functions and lines of code that consume the most memory. This is particularly useful for identifying memory leaks or inefficiencies in custom code or plugins.
- Checking WordPress Admin Pages: Some plugins, particularly those that perform resource-intensive tasks in the admin area, can consume significant memory. Monitoring the memory usage when accessing admin pages can help identify these plugins.
- Reviewing the `wp-config.php` file: Checking the `wp-config.php` file to identify any custom memory limit configurations. If the memory limit is set too low, it can cause issues.
Isolating the Problematic Plugin or Theme
Isolating the plugin or theme responsible for high memory consumption involves a systematic approach to identify the culprit. This process typically involves disabling plugins and themes one by one to determine their impact on memory usage.
- Create a Backup: Before making any changes, create a complete backup of your website. This allows you to restore your website to its previous state if any issues arise during the troubleshooting process.
- Disable All Plugins: Begin by deactivating all plugins. This provides a baseline for your website's memory usage. If the memory limit errors disappear after disabling all plugins, the issue is likely related to a plugin.
- Enable Plugins One by One: Activate each plugin individually, testing the website's performance and monitoring memory usage after each activation. After enabling each plugin, test the website by browsing different pages, checking the admin area, and performing any relevant actions. Monitor the memory usage using a debugging plugin or by checking server logs for any memory limit errors.
- Identify the Culprit: When you enable a plugin and the memory limit errors reappear, that plugin is the likely cause of the issue. If the problem occurs after activating a specific plugin, you have found the culprit.
- Test the Theme: If disabling all plugins doesn't resolve the issue, temporarily switch to a default WordPress theme, such as Twenty Twenty-Three. If the memory limit errors disappear, the theme may be the problem.
- Check Theme Functions: If the theme is the issue, review the theme's code, especially the `functions.php` file, for any custom code that might be causing memory issues.
- Repeat the Process: If the issue persists, repeat the process, testing each plugin and theme individually. It is a good idea to disable all plugins and then activate them one by one, monitoring memory usage after each activation.
Step-by-Step Guide to Disable Plugins and Themes
Following a structured approach when disabling plugins and themes is essential for effectively isolating the source of memory limit issues.
- Access the WordPress Admin Dashboard: Log in to your WordPress website's admin dashboard.
- Navigate to the Plugins Page: In the left-hand navigation menu, click on "Plugins" and then "Installed Plugins."
- Deactivate All Plugins (Initially): Select all plugins by checking the box at the top of the plugin list. Then, from the "Bulk actions" dropdown, select "Deactivate" and click "Apply." This will deactivate all plugins simultaneously.
- Test Website Performance: After deactivating all plugins, test your website's performance. If the memory limit errors are resolved, the issue is related to one of the plugins.
- Activate Plugins One by One: Return to the "Installed Plugins" page. Activate each plugin individually by clicking the "Activate" link under the plugin's name.
- Monitor Memory Usage: After activating each plugin, monitor your website's memory usage using a debugging plugin, server logs, or by observing any error messages.
- Identify the Problem Plugin: If memory limit errors reappear after activating a specific plugin, that plugin is likely the cause. Deactivate the problematic plugin.
- Switch Themes (If Necessary): If disabling all plugins does not resolve the issue, navigate to "Appearance" and then "Themes." Activate a default WordPress theme (e.g., Twenty Twenty-Three). Test the website's performance.
- Analyze the Theme (If Necessary): If the issue is related to the theme, review the theme's code for any custom functions or scripts that might be causing memory issues.
Increasing the PHP Memory Limit
Addressing WordPress PHP memory limit issues often requires increasing the allocated memory. This section details various methods to increase the PHP memory limit, providing instructions and considerations for each approach. Choosing the appropriate method depends on your hosting environment and level of access.
Modifying the `wp-config.php` File
One of the most common and straightforward methods for increasing the PHP memory limit is by modifying the `wp-config.php` file, which is located in the root directory of your WordPress installation. This file contains essential configuration settings for your WordPress site.
To increase the memory limit, you need to add a specific line of code within the `wp-config.php` file. This code defines the maximum amount of memory PHP scripts are allowed to use.
Here's how to do it:
1. Access the `wp-config.php` file: You can access this file via FTP (File Transfer Protocol) using a client like FileZilla, through your hosting control panel's file manager, or via SSH (Secure Shell) if you have command-line access.
2. Open the file for editing: Locate the `wp-config.php` file and open it in a text editor.
3.
Add the memory limit definition: Add the following line of code
-before* the line that says "/* That's all, stop editing! Happy blogging.
-/" or similar. This line sets the memory limit to 256MB:
```php
define( 'WP_MEMORY_LIMIT', '256M' );
```
You can adjust the value ('256M' in this example) to a higher value, such as '512M' or '1024M', depending on your needs and hosting limitations.
4. Save the changes: Save the `wp-config.php` file after adding the code.
5. Upload the file: If you edited the file locally, upload it back to your server, overwriting the existing file.
This method is generally effective but may be overridden by server-level configurations in some hosting environments.
Modifying the `.htaccess` File
The `.htaccess` file is a powerful configuration file used by Apache web servers to control various aspects of the server's behavior. It can also be used to increase the PHP memory limit.
To modify the `.htaccess` file:
1. Access the `.htaccess` file: Similar to the `wp-config.php` file, you can access the `.htaccess` file via FTP, your hosting control panel's file manager, or SSH. The `.htaccess` file is usually located in the root directory of your WordPress installation.
-Note:* If you can't find the `.htaccess` file, it may be hidden. In your FTP client or file manager, enable the option to show hidden files.
2. Open the file for editing: Open the `.htaccess` file in a text editor.
3. Add the PHP memory limit directive: Add the following line of code to the file. This line sets the PHP memory limit to 256MB:
```apache
php_value memory_limit 256M
```
You can adjust the value ('256M') to a higher value, such as '512M' or '1024M'.
4. Save the changes: Save the `.htaccess` file.
5. Upload the file: If you edited the file locally, upload it back to your server, overwriting the existing file.
This method is effective for Apache servers but may not work on other server types (e.g., Nginx). It can also be overridden by server-level configurations. Be cautious when modifying `.htaccess` as incorrect changes can potentially break your website. Always back up the file before making any changes.
Contacting the Hosting Provider
If you're unable to increase the PHP memory limit using the methods above, or if you're unsure how to proceed, the best course of action is to contact your hosting provider. They have direct access to the server configuration and can make the necessary changes for you.
To contact your hosting provider:
1. Identify your hosting provider's support channels: Most hosting providers offer support via email, phone, and/or live chat. Locate their support contact information on their website or in your hosting account dashboard.
2. Explain the issue clearly: Explain that you're encountering PHP memory limit issues on your WordPress site and that you need the memory limit increased.
3. Provide details about your website: Mention the URL of your website and any specific plugins or themes that are causing the memory issues, if known.
4. Request the desired memory limit: Request a specific memory limit, such as 256MB, 512MB, or 1024MB, depending on your needs. Your hosting provider can advise you on the appropriate limit for your hosting plan.
Hosting providers are generally very helpful with these types of requests. They often have pre-defined procedures for increasing memory limits.
Comparison of Methods
Here's a comparison of the methods discussed above, including their pros, cons, and considerations:
```html
| Method | Pros | Cons | Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Modifying `wp-config.php` |
|
|
|
| Modifying `.htaccess` |
|
|
|
| Contacting Hosting Provider |
|
|
|
```
This table provides a clear overview of each method's advantages and disadvantages, helping you choose the best approach for your situation. Remember to test your website after making any changes to ensure it's functioning correctly.
Optimizing WordPress for Memory Efficiency
To effectively manage and reduce WordPress memory usage, optimizing various aspects of your website is crucial. This involves streamlining plugins, themes, images, and leveraging caching mechanisms. By implementing these strategies, you can significantly improve your site's performance, reduce memory consumption, and prevent memory-related errors.
Optimizing Plugins and Themes
Plugins and themes can be significant consumers of memory. Optimizing them is a key step in reducing overall memory usage. This involves evaluating their code, functionality, and resource usage.
Optimizing plugins and themes involves several key areas:
- Code Review and Optimization: Examine the code for inefficiencies, such as unnecessary loops, excessive database queries, and inefficient algorithms. Code optimization is crucial for reducing memory footprint. Consider using tools like PHP Code Sniffer or PHPStan to identify potential code quality issues.
- Plugin Selection: Choose plugins that are well-coded, actively maintained, and have a good reputation. Poorly coded plugins can quickly bloat memory usage. Research plugin reviews and check their resource consumption before installing.
- Theme Optimization: Ensure your theme is lightweight and well-coded. Avoid themes with excessive features or bloat. Consider using a theme framework known for its performance, such as GeneratePress or Astra.
- Deactivate and Delete Unused Plugins: Regularly review your installed plugins and deactivate and delete any that are not in use. Even inactive plugins can consume resources.
- Keep Plugins and Themes Updated: Regularly update plugins and themes to the latest versions. Updates often include performance improvements and bug fixes that can reduce memory usage.
Plugin Optimization Techniques
Several techniques can be used to optimize plugins specifically to reduce their memory footprint. Implementing these methods can lead to significant improvements in performance.
One example of a plugin optimization technique is lazy loading.
- Lazy Loading: Implement lazy loading for images, videos, and other resources. Lazy loading delays the loading of resources until they are needed, reducing initial page load time and memory consumption. Many plugins offer lazy loading functionality.
- Optimize Database Queries: Ensure plugins use efficient database queries. Avoid unnecessary queries and optimize existing ones.
- Reduce Object Instantiation: Minimize the creation of unnecessary objects. Efficient object management reduces memory overhead.
- Cache Data: Cache frequently accessed data to reduce the need for repeated calculations or database queries. Use WordPress's built-in caching mechanisms or dedicated caching libraries.
- Code Minification: Minify plugin code (CSS and JavaScript) to reduce file sizes and improve loading times. Minification removes unnecessary characters from the code without changing its functionality.
Optimizing Images
Images often contribute significantly to memory consumption. Optimizing images is a critical step in improving WordPress performance.
Image optimization includes:
- Image Compression: Compress images to reduce their file size without significantly impacting their quality. Use image compression tools like TinyPNG, ShortPixel, or Smush.
- Image Format Selection: Choose the appropriate image format for each image. Use JPEG for photographs, PNG for images with transparency, and WebP for superior compression and quality.
- Image Resizing: Resize images to the appropriate dimensions for their display on your website. Avoid uploading large images that are unnecessarily scaled down.
- Use a CDN (Content Delivery Network): A CDN distributes your images across multiple servers, reducing load times and freeing up server resources.
- Optimize Image Metadata: Remove unnecessary metadata from images. Metadata can increase file size.
Using a Caching Plugin
Caching plugins play a crucial role in improving WordPress performance and reducing memory load. They store pre-rendered versions of your pages, reducing the amount of processing required each time a user visits your site.
Caching plugins function by:
- Page Caching: Caching plugins store static HTML versions of your pages, which are served to users instead of dynamically generating them. This significantly reduces server load and memory usage.
- Object Caching: Cache database queries and other frequently accessed data to reduce the load on your database.
- Browser Caching: Set browser caching headers to instruct users' browsers to store static assets, such as images and CSS files, locally.
- Minification and Concatenation: Minify and concatenate CSS and JavaScript files to reduce file sizes and the number of HTTP requests.
- CDN Integration: Many caching plugins integrate with CDNs to further improve performance by serving content from servers closer to the user.
Best Practices to Improve WordPress Performance
Implementing best practices is crucial for maintaining optimal WordPress performance and reducing memory usage. These practices involve a holistic approach to website management.
Best practices include:
- Choose a Reliable Hosting Provider: Select a hosting provider that offers sufficient resources and optimized WordPress environments.
- Use a Lightweight Theme: Opt for a fast, well-coded theme. Avoid themes with excessive features or bloat.
- Optimize Database: Regularly optimize your WordPress database to remove unnecessary data and improve performance. Use plugins like WP-Optimize or Advanced Database Cleaner.
- Monitor Performance: Regularly monitor your website's performance using tools like Google PageSpeed Insights or GTmetrix.
- Enable Gzip Compression: Enable Gzip compression to compress files before they are sent to the user's browser.
- Limit Post Revisions: Limit the number of post revisions stored in your database to prevent database bloat.
- Use PHP 7.4 or Higher: Ensure you are using a supported version of PHP, such as 7.4 or higher, for performance and security benefits.
- Implement a Security Plugin: Use a security plugin to protect your website from malicious attacks.
Troubleshooting Common Problems
Memory limit issues in WordPress can manifest in various ways, causing frustration and hindering website functionality. This section delves into common problems and offers practical solutions to help you diagnose and resolve these issues effectively. Addressing these specific scenarios will improve your WordPress site's stability and performance.
Handling Errors Related to Image Uploads
Image upload errors are a frequent symptom of insufficient memory. These errors can prevent users from adding new content or updating existing posts.
The most common errors related to image uploads include:
- HTTP Error: This is a general error often indicating a memory limit issue. The server might not have enough resources to process the image during upload.
- "Upload failed" or "Image could not be processed": These messages suggest the server is unable to handle the image's size or format due to memory constraints.
- White screen of death (WSOD): In severe cases, insufficient memory can lead to the WSOD, where the entire WordPress admin area becomes inaccessible after attempting an image upload.
To address these issues:
- Increase the PHP Memory Limit: As discussed previously, increasing the memory limit in your `wp-config.php` file or through your hosting control panel is often the first step. Consider setting the limit to 256MB or even 512MB if you frequently work with large images.
- Optimize Images Before Uploading: Before uploading, compress images using tools like TinyPNG or ShortPixel. This reduces file sizes, minimizing the memory needed for processing. For example, a 5MB image can be reduced to 500KB without a significant loss of quality.
- Check Image Dimensions: Ensure images are not excessively large in terms of their dimensions (width and height). Resizing images to fit your website's layout before uploading reduces the server's processing load. A website using a 1200px width design might not need images larger than 1200px wide.
- Use a CDN (Content Delivery Network): A CDN can offload image processing and serving from your server, reducing the strain on your memory. Services like Cloudflare or Amazon CloudFront can efficiently handle image delivery.
- Review Your Server Configuration: Check your server's settings for upload limits. These settings can sometimes override the PHP memory limit, preventing successful uploads. You may need to adjust these settings through your hosting provider's control panel.
- Troubleshoot Plugin Conflicts: Some plugins, especially those related to image optimization or galleries, can consume significant memory during uploads. Deactivate plugins one by one to identify potential conflicts.
Solutions for Memory-Related Issues During Plugin Installations or Updates
Plugin installations and updates often require significant memory resources, especially if the plugin is large or complex. Insufficient memory can lead to failed installations, broken websites, or the inability to update existing plugins.
Here are the common memory-related issues during plugin installations or updates and how to solve them:
- Installation Fails with Error Messages: The most common error is a message stating the installation failed due to memory exhaustion. This is a direct indication that the PHP memory limit is insufficient.
- White Screen of Death (WSOD) During Installation: Similar to image uploads, the WSOD can occur during plugin installations if the memory limit is exceeded. This can render your website inaccessible.
- Partial Plugin Installation: The plugin may install partially, leading to functionality issues or broken features. This can happen when the installation process is interrupted due to memory limits.
- Update Failures: Existing plugins may fail to update, displaying error messages indicating a lack of resources.
To address these issues:
- Increase the PHP Memory Limit: Increase the memory limit to a higher value (e.g., 256MB or 512MB) in your `wp-config.php` file or through your hosting control panel. This is the most direct solution.
- Deactivate Unnecessary Plugins: Before installing or updating plugins, deactivate any plugins you're not actively using. This frees up memory resources.
- Check for Plugin Conflicts: Conflicting plugins can consume excessive memory. Try deactivating plugins one by one to identify the culprit.
- Install Plugins in Batches: If you're installing multiple plugins, try installing them in smaller batches. This prevents the server from being overwhelmed.
- Use the Default WordPress Theme: Temporarily switch to a default WordPress theme (e.g., Twenty Twenty-Three) to eliminate theme-related memory issues.
- Contact Your Hosting Provider: If you've increased the memory limit and still encounter problems, contact your hosting provider. They may have server-side limitations or other configurations that are causing the issue.
- Manually Install Plugins: If the installation fails repeatedly, download the plugin files from the WordPress repository and manually upload them via FTP or your hosting provider's file manager.
Strategies for Dealing with Memory Exhaustion During Theme Customization
Theme customization, especially with complex themes and page builders, can consume significant memory. Memory exhaustion during customization can lead to slow performance, errors, and the inability to save changes.
Here are some strategies to mitigate memory exhaustion during theme customization:
- Increase the PHP Memory Limit: Start by increasing the memory limit in your `wp-config.php` file. A higher memory limit is often essential when working with advanced themes.
- Use a Child Theme: Always use a child theme when customizing a parent theme. This prevents your customizations from being overwritten during theme updates and can sometimes improve performance.
- Optimize Theme Code and Assets: If you're comfortable with code, review your theme's code for inefficiencies. Remove unnecessary code, and optimize CSS and JavaScript files. Minify these files to reduce their size.
- Deactivate Unnecessary Plugins: Temporarily deactivate plugins that aren't essential to the customization process. This frees up memory.
- Use a Lightweight Page Builder (or None): Consider using a lightweight page builder, or avoid using a page builder altogether if your theme allows for native customization. Page builders can be memory-intensive.
- Reduce the Number of Revisions: WordPress saves revisions of your posts and pages, which can consume database space and memory. Limit the number of revisions saved in your `wp-config.php` file:
define( 'WP_POST_REVISIONS', 3 );This will limit the number of revisions to 3.
- Optimize Images: As with image uploads, optimize all images used in your theme's customization. Compress images and ensure they are appropriately sized for their display areas.
- Monitor Server Resource Usage: Use your hosting control panel or a server monitoring plugin to track your server's memory usage during customization. This helps you identify when you're approaching the memory limit.
- Break Down Complex Customizations: If you're making extensive customizations, break them down into smaller, manageable steps. Save your work frequently to prevent data loss.
- Consider a More Resourceful Hosting Plan: If you consistently run into memory issues during theme customization, you may need to upgrade to a hosting plan with more memory and processing power.
Advanced Techniques and Considerations
![How to Increase WordPress PHP Memory Limit [4 Easy Methods] How to Increase WordPress PHP Memory Limit [4 Easy Methods]](https://teknocode.web.id/wp-content/uploads/2025/10/Adjusting-PHP-Memory-Limit-via-.htaccess-1.png)
Optimizing WordPress memory usage is an ongoing process. Beyond basic adjustments, advanced techniques can significantly improve performance and stability. These techniques involve deeper analysis and proactive measures to manage memory effectively, preventing issues before they impact the website's functionality. This section delves into these advanced strategies.
Advanced Memory Management Techniques
Effective memory management goes beyond simply increasing the PHP memory limit. It involves proactive measures to control memory consumption and prevent potential issues.
- Object Caching: Implement object caching, preferably using a persistent object cache like Redis or Memcached. This stores frequently accessed data in memory, reducing database queries and server load. For example, a large e-commerce site with thousands of products can benefit significantly, as object caching can dramatically reduce the number of database calls needed to display product information. This minimizes the memory used by database interactions.
- Code Optimization: Regularly review and optimize WordPress code, including themes and plugins. Inefficient code can lead to memory leaks and excessive memory usage. For example, a poorly written plugin might load large amounts of data unnecessarily, or a theme might include redundant functions. Regularly audit your code for potential optimizations.
- Database Optimization: Optimize the WordPress database to remove unnecessary data, such as post revisions and spam comments. Large databases consume more memory. For instance, a blog with years of posts and many revisions can significantly reduce its database size by limiting the number of post revisions stored.
- Lazy Loading: Implement lazy loading for images and other media. This technique loads content only when it's needed, reducing initial page load times and memory usage. For example, a page with many high-resolution images can benefit from lazy loading, as images are loaded only as the user scrolls down the page.
- PHP Workers: Consider using PHP workers or a task queue system (e.g., WP-Cron alternative) for resource-intensive tasks. This offloads tasks to background processes, preventing them from consuming memory during page requests.
Using Debugging Tools to Pinpoint Memory Leaks
Identifying memory leaks requires the use of specialized debugging tools. These tools provide insights into memory allocation and deallocation, helping to pinpoint the source of leaks.
- Xdebug: Xdebug is a popular PHP extension that provides debugging and profiling capabilities. It allows you to track memory usage, identify memory leaks, and profile code performance. For example, using Xdebug, you can trace the execution of a specific function and see how much memory it allocates and whether it's properly deallocated.
- Blackfire.io: Blackfire.io is a performance monitoring tool that provides detailed insights into code performance and memory usage. It can help identify bottlenecks and memory leaks. It offers a visual representation of memory allocation over time, allowing you to identify areas where memory is growing unexpectedly.
- PHP Memory Profilers: Various PHP memory profilers can track memory allocation and deallocation. These tools can provide detailed reports on memory usage by functions and classes. These tools generate reports that can pinpoint the exact lines of code causing memory leaks.
- Monitoring Plugins: Utilize WordPress plugins designed for monitoring memory usage and identifying potential issues. Some plugins can alert you to excessive memory consumption or other performance problems. For instance, a plugin might detect a sudden spike in memory usage and alert you to investigate the cause.
The Impact of PHP Versions on Memory Usage
Different PHP versions have varying memory management capabilities and performance characteristics. Upgrading to a newer PHP version can often lead to improvements in memory usage and overall performance.
- PHP 7.x vs. PHP 8.x: PHP 7.x introduced significant performance improvements compared to PHP 5.x, including improved memory usage. PHP 8.x further enhances performance and memory efficiency, particularly with the introduction of features like JIT (Just-In-Time) compilation. For example, a website running on PHP 8.x might experience faster page load times and reduced memory consumption compared to the same website running on PHP 7.4.
- Garbage Collection: PHP's garbage collection mechanism is responsible for automatically freeing up memory that's no longer needed. Newer PHP versions often have improved garbage collection algorithms, leading to more efficient memory management.
- Performance Benchmarks: Refer to performance benchmarks and real-world examples when comparing different PHP versions. These benchmarks can provide data on memory usage and execution times. For instance, you can find online comparisons showing the memory usage of different PHP versions running the same WordPress code.
Analyzing Server Logs for Memory-Related Errors
Server logs contain valuable information about memory-related errors, which can help diagnose and resolve issues. Regularly reviewing these logs is essential for proactive memory management.
- Error Logs: The PHP error log (usually named `error_log` or within the server's error logs) records errors, warnings, and notices. Look for entries related to memory exhaustion, such as "Allowed memory size exhausted" or "Out of memory". These messages indicate that the PHP script has exceeded its memory limit.
- Access Logs: Access logs record all requests to the server. Analyze these logs to identify pages or actions that might be consuming excessive memory. For example, a specific page might be consistently generating "Allowed memory size exhausted" errors, indicating a problem with that page's code or content.
- Slow Query Logs: The slow query log records database queries that take longer than a specified time. Slow queries can contribute to memory usage. Optimizing slow queries can improve performance and reduce memory consumption.
- Log Analysis Tools: Utilize log analysis tools to automate the process of searching and analyzing server logs. These tools can identify patterns and anomalies related to memory usage. For example, a log analysis tool might automatically flag pages that are consistently generating memory errors.
Descriptive Illustration of WordPress Architecture and Memory Allocation Processes
The WordPress architecture and memory allocation process can be visualized to better understand how memory is used. This description will provide a clear picture without using image links.
The illustration presents a simplified model of WordPress's memory usage, starting with the web server (e.g., Apache or Nginx) at the top. The web server receives requests from users.
1. Web Server: The web server receives HTTP requests. It then passes these requests to the PHP interpreter.
2. PHP Interpreter: The PHP interpreter loads the WordPress core files, theme files, and plugin files.
It then begins processing the PHP code.
3. WordPress Core: The WordPress core is the central component of the platform, responsible for managing posts, pages, users, and other functionalities.
4. Themes and Plugins: Themes control the visual appearance of the website, and plugins extend its functionality.
Both themes and plugins can contain PHP code that consumes memory.
5. Database Interaction: WordPress interacts with a database (typically MySQL) to store and retrieve data. Database queries can consume significant memory.
6.
Memory Allocation: The PHP interpreter allocates memory to store data, variables, and objects. The amount of memory allocated is governed by the PHP memory limit.
7. Memory Consumption Tracking: Tools like Xdebug or Blackfire can monitor the memory consumption of different components, identifying memory leaks or inefficiencies.
8.
PHP Processes: Each request to the server generates a PHP process. These processes allocate and release memory as the request is processed.
9. Garbage Collection: PHP's garbage collector automatically frees up memory that is no longer in use, preventing memory leaks.
1
0.
Response to User: After processing, the server returns the rendered HTML to the user's browser.
The entire process can be compared to a chain, with each link (component) contributing to the overall memory usage. If one link (e.g., a plugin) consumes too much memory, it can break the chain (leading to an out-of-memory error). The memory limit acts as a safety net, preventing the chain from breaking completely. Understanding this chain and the flow of memory helps identify and address memory-related issues effectively.
Monitoring and Maintenance
Regular monitoring and proactive maintenance are crucial for preventing and resolving WordPress PHP memory limit issues. They provide insights into your website's resource consumption and allow you to address problems before they impact performance or cause downtime. This section Artikels the importance of ongoing monitoring, alert setup, maintenance scheduling, and the utilization of server monitoring tools.
Importance of Ongoing Memory Usage Monitoring
Continuous monitoring of memory usage allows you to identify trends, detect anomalies, and proactively address potential memory limit problems. This proactive approach minimizes the risk of website slowdowns, errors, and outages.
Setting Up Alerts for Memory Limit Issues
Implementing alerts provides immediate notification of memory limit breaches, allowing for rapid response and mitigation. This proactive approach helps minimize downtime and data loss.
To set up effective alerts, consider the following:
- Thresholds: Define specific memory usage thresholds. For example, set an alert to trigger when memory consumption reaches 80% of the PHP memory limit. This provides a buffer for fluctuations.
- Alerting Methods: Choose an appropriate alerting method, such as email notifications, SMS messages, or integration with a monitoring dashboard.
- Monitoring Tools: Utilize server monitoring tools that provide real-time memory usage data and alert capabilities. Common tools include:
- New Relic: A comprehensive application performance monitoring (APM) platform.
- Datadog: A cloud-scale monitoring and analytics platform.
- Prometheus and Grafana: Open-source tools for monitoring and visualization.
- ServerPilot: A server management panel that provides basic monitoring.
- Alert Response: Establish a clear response plan for when alerts are triggered, including identifying the cause of the memory spike and implementing appropriate solutions.
Implementing a Regular Maintenance Schedule to Prevent Memory Problems
A well-defined maintenance schedule helps prevent memory problems by addressing potential issues proactively. Regular maintenance minimizes the risk of memory leaks and ensures optimal performance.
Consider the following elements for your maintenance schedule:
- Plugin Updates: Regularly update all plugins to ensure compatibility and security. Outdated plugins can sometimes contribute to memory leaks or inefficiencies.
- Theme Updates: Keep your theme updated for the same reasons as plugins.
- Database Optimization: Optimize your WordPress database regularly. This includes cleaning up orphaned data, optimizing tables, and removing unnecessary overhead. Use plugins like WP-Optimize or the database optimization tools provided by your hosting provider.
- File Cleanup: Remove unnecessary files, such as old backups, unused themes, and inactive plugins. These files can consume disk space and potentially contribute to memory issues.
- Log Monitoring: Regularly review your server and WordPress error logs for any memory-related errors or warnings. These logs provide valuable insights into potential problems.
- Performance Testing: Periodically test your website's performance using tools like GTmetrix or Google PageSpeed Insights. This helps identify areas for improvement and detect potential memory bottlenecks.
- Scheduled Backups: Implement a reliable backup strategy to protect your website data. Backups can be essential for restoring your site in case of memory-related errors.
Using Server Monitoring Tools to Track Memory Consumption Over Time
Server monitoring tools provide detailed insights into memory consumption patterns, allowing for data-driven decision-making. They help identify trends, pinpoint resource-intensive processes, and optimize your WordPress website for efficiency.
Here's how to effectively utilize server monitoring tools:
- Real-time Monitoring: Monitor memory usage in real-time to observe immediate impacts of changes and identify instantaneous spikes.
- Historical Data Analysis: Analyze historical data to identify trends and patterns in memory consumption over time. This helps you understand how your website's memory usage changes.
- Process Identification: Use the tools to identify which processes are consuming the most memory. This can help you pinpoint the source of memory leaks or inefficiencies.
- Performance Metrics: Track other relevant performance metrics, such as CPU usage, disk I/O, and database query times. Correlating these metrics with memory usage can provide a more comprehensive understanding of your website's performance.
- Alerting and Notifications: Set up alerts to notify you of unusual memory usage patterns or when memory limits are reached.
- Examples of Tools: As mentioned earlier, tools like New Relic, Datadog, and Prometheus with Grafana are valuable for this purpose. Many hosting providers also offer built-in monitoring tools.
For instance, a website experiencing a gradual increase in memory usage over several weeks might indicate a memory leak in a plugin or theme. By analyzing historical data, you can pinpoint the time when the memory usage began to increase and correlate it with any recent plugin updates or code changes. This information helps you identify the problematic code and implement a fix.
Closing Notes
In conclusion, mastering the art of debugging WordPress PHP memory limit issues is crucial for maintaining a healthy and high-performing website. By understanding the underlying causes, employing effective diagnostic techniques, and implementing proactive optimization strategies, you can ensure your WordPress site operates at its full potential. Remember to continuously monitor your site's memory usage and adapt your approach as your website evolves, ensuring a seamless and enjoyable experience for your visitors.