Learning how to code in Python using Visual Studio Code editor opens the door to an efficient and user-friendly programming environment suitable for beginners and experienced developers alike. This comprehensive guide walks you through the essential steps to set up, write, and manage Python projects with confidence and ease.
From installing Python on various operating systems to configuring Visual Studio Code for optimal development, this overview provides clear instructions and best practices to help you start coding effectively. Whether you’re aiming to develop simple scripts or complex applications, mastering this setup will significantly enhance your programming experience.
Understanding the Basics of Python Programming
Python has become one of the most popular programming languages due to its simplicity, readability, and versatility. Before diving into advanced projects, mastering the fundamental concepts of Python syntax and structure is essential. This foundation allows programmers to write efficient code, debug effectively, and expand their skills with confidence. Whether you are automating tasks, analyzing data, or developing web applications, a solid grasp of core Python principles is indispensable.
In this section, we will explore the basic syntax rules, the process of installing Python across different operating systems, methods to verify the installation, and an organized overview of fundamental Python statements and their typical usage. This comprehensive overview aims to empower new learners with the essential knowledge needed to start coding proficiently in Python using Visual Studio Code or any other preferred editor.
Core Concepts of Python Syntax and Structure
Python’s syntax emphasizes readability and simplicity, making it accessible for beginners and powerful enough for advanced developers. The language uses indentation to define code blocks instead of braces or s, which enforces clean and uniform code formatting. Python supports multiple programming paradigms, including procedural, object-oriented, and functional programming, providing flexibility for various development needs.
Key syntax features include:
- Variables and Data Types: Python dynamically assigns data types to variables, eliminating the need for explicit declarations. Common data types include integers, floats, strings, lists, dictionaries, and booleans.
- Control Structures: Conditional statements such as
if,elif,else, and loops likeforandwhilefacilitate decision-making and iteration in code. - Functions: Defined using the
def, functions enable code reuse and modular programming. Arguments can be passed, and functions can return values. - Indentation: Indentation (typically four spaces) is mandatory in Python to define code blocks, making code structure clear and consistent.
- Comments: Single-line comments start with
#, and multi-line comments can be enclosed within triple quotes ('''or""").
Installing Python on Various Operating Systems
To begin coding in Python, installing the interpreter is the initial step. The process varies depending on the operating system, but the overall procedure involves downloading the latest version from the official Python website and following setup instructions specific to your environment.
The main operating systems include Windows, macOS, and Linux. Below are summarized installation steps for each:
Windows
- Visit the official Python download page at python.org .
- Download the latest Windows installer compatible with your system architecture (32-bit or 64-bit).
- Run the installer and ensure the option Add Python to PATH is checked before proceeding.
- Complete the installation by following on-screen prompts.
macOS
- Download the latest Python installer for macOS from the official website.
- Open the downloaded
.pkgfile and follow the installer instructions. - You can also install Python via Homebrew by opening Terminal and executing:
brew install python
.
Linux
- Most Linux distributions come with Python pre-installed. To verify, open the terminal and type
python3 –version
.
- If not installed or an update is needed, use the package manager specific to your distribution.
- For Ubuntu/Debian, run:
sudo apt update && sudo apt install python3
.
- For Fedora, run:
sudo dnf install python3
.
Verifying Python Installation
After installation, it is crucial to verify that Python has been installed correctly and is accessible from the command line. This ensures that you can run Python scripts and use the interpreter from your preferred terminal or command prompt.
Follow these simple steps to confirm the installation:
- Open your command line interface:
- Windows: Command Prompt or PowerShell
- macOS/Linux: Terminal
- Type the command:
python –version
If Python is installed correctly, the terminal will display the version number, such as Python 3.10.2. Alternatively, typing python3 --version can also confirm the installation, especially on Linux or macOS systems where Python 2 may still be present.
To launch the Python interactive shell, type:
python
or
python3
If the Python prompt (>>> ) appears, the installation is successful, and you are ready to start coding.
Fundamental Python Statements and Their Usage
Understanding basic Python statements is essential for writing functional programs. Below is an organized table outlining common statements, their syntax, and usage scenarios:
| Statement | Syntax Example | Usage Description |
|---|---|---|
| Assignment | variable = value |
Assigns a value to a variable, enabling storage and manipulation of data. |
| Conditional | if condition: |
Executes code blocks based on whether a condition evaluates to True. |
| Loop (for) | for item in iterable: |
Iterates over elements in a sequence such as lists, tuples, or strings. |
| Loop (while) | while condition: |
Repeats a block of code as long as the condition remains True. |
| Function Definition | def function_name(parameters): |
Creates reusable blocks of code that can be called multiple times. |
| Print Statement | print("Hello, World!") |
Outputs information to the console or terminal. |
| Import Module | import module_name |
Includes external libraries or modules within your script for extended functionality. |
Setting Up Visual Studio Code for Python Development
Effective Python development begins with a well-configured environment. Visual Studio Code (VS Code) is a popular, lightweight, and versatile code editor that supports Python programming through extensions and customizable settings. Proper setup ensures a smooth coding experience, efficient debugging, and seamless project management, making it essential for both beginners and experienced developers.
Configuring VS Code specifically for Python involves downloading and installing the editor, adding relevant extensions, and setting up the Python interpreter. These steps optimize the editor for Python syntax highlighting, code completion, debugging, and other essential features, thereby accelerating development workflows and reducing potential errors.
Downloading and Installing Visual Studio Code
To begin, obtaining the latest version of Visual Studio Code ensures compatibility with all features and extensions. The process involves accessing the official website, choosing the appropriate installer based on your operating system, and following installation prompts.
- Navigate to the official Visual Studio Code website at https://code.visualstudio.com/ .
- Select the download link corresponding to your operating system: Windows, macOS, or Linux.
- Once the installer is downloaded, run the setup file and follow the on-screen instructions. For Windows, this involves agreeing to the license, choosing the installation directory, and selecting optional components like adding VS Code to PATH or creating desktop icons.
- Complete the installation process and launch Visual Studio Code.
After installation, it’s advisable to restart your system to ensure all environment variables are correctly configured, especially on Windows, to facilitate command-line access and extension management.
Installing the Python Extension in Visual Studio Code
The core functionality for Python development in VS Code is provided by the Python extension, which offers features like syntax highlighting, code navigation, IntelliSense, linting, debugging, and testing.
To enhance your coding environment, follow these steps:
- Open Visual Studio Code.
- Access the Extensions view by clicking on the Extensions icon in the Activity Bar on the side of the window or pressing
Ctrl+Shift+X. - In the search bar, type “Python” to locate the extension developed by Microsoft.
- Select the Python extension from the search results and click the “Install” button.
- Once installed, VS Code will prompt you to reload or restart to activate the extension fully.
Additionally, it is recommended to install other useful extensions like Pylance for improved language support, and Python Test Explorer for managing unit tests.
Configuring the Python Interpreter within Visual Studio Code
Setting the correct Python interpreter is crucial for ensuring that your scripts run with the desired Python version and environment. This is especially important when working with virtual environments or multiple Python installations.
The configuration process involves selecting the interpreter specific to your project or workspace, which enables VS Code to utilize the correct Python executable for execution and debugging tasks.
- Open your project folder in Visual Studio Code.
- Press
Ctrl+Shift+Pto open the Command Palette. - Type “Python: Select Interpreter” into the palette and select the command when it appears.
- A list of available Python interpreters will be displayed. This list includes global installations, virtual environments, and conda environments.
- Select the interpreter that corresponds to your preferred Python version or environment.
If you are using a virtual environment, ensure it is activated before selecting it within VS Code. This guarantees that all dependencies and packages are correctly associated with your project.
Visual Flowchart for Setting Up VS Code for Python
A comprehensive setup flowchart for new users would illustrate the following steps: starting from downloading VS Code, installing essential extensions like Python, setting the correct interpreter, and configuring project-specific settings. The flowchart should visually depict decision points such as choosing between different Python environments, enabling debugging options, and integrating version control systems. This visual guide simplifies onboarding and ensures users follow a logical setup sequence, reducing setup errors and enhancing productivity.
Creating and Managing Python Projects in Visual Studio Code
Efficient project management within Visual Studio Code (VS Code) is essential for maintaining organized, scalable, and easily navigable Python development workflows. Properly initiating new projects, organizing files, and managing virtual environments are foundational skills that streamline coding efforts and facilitate collaboration. This section provides detailed guidance on creating project folders, structuring your workspace, and handling virtual environments directly within VS Code to optimize your Python programming experience.
Establishing a well-structured project environment helps in maintaining clarity, reducing errors, and ensuring reproducibility. By following best practices for organizing project files and managing dependencies through virtual environments, developers can create robust Python applications suitable for both small scripts and large-scale projects.
Initiating a New Python Project Folder and Workspace
Starting a new Python project in Visual Studio Code begins with creating a dedicated folder that serves as the central workspace for your project files. This approach ensures that all related scripts, data, and configurations are contained in a single location, making management straightforward and logical.
- Open Visual Studio Code and select the ‘File’ menu, then choose ‘Open Folder’ to create or select an existing directory on your computer.
- If creating a new project, click ‘New Folder’ in your file explorer, name it appropriately (e.g., ‘MyPythonProject’), and open it within VS Code.
- Once the folder is open, VS Code automatically recognizes it as a workspace, enabling you to save your project files within this directory and utilize workspace settings if necessary.
To enhance your workflow, consider saving the workspace configuration by navigating to File > Save Workspace As…. This allows you to quickly reopen your project with all settings and folder configurations preserved, especially when working across multiple projects.
Creating and Saving Python Script Files
With a project folder in place, the next step involves creating Python script files that contain your code. Proper file management ensures that scripts are easily identifiable and accessible.
- Within your project folder in VS Code, click the ‘New File’ icon or right-click the folder in the Explorer panel and select ‘New File.’
- Name the file with a descriptive name ending with the .py extension, such as
main.pyordata_analysis.py. - Begin coding within the newly created file. To save your work, press Ctrl + S (Windows/Linux) or Cmd + S (macOS) or select ‘File > Save.’
- It is advisable to save frequently and use meaningful filenames to facilitate project navigation and debugging.
Organizing scripts into subfolders such as src for source code, tests for testing scripts, and data for datasets promotes clarity and scalability, especially in larger projects.
Organizing Project Structure with Folders and Files
A logical project structure enhances maintainability and collaboration. The following table illustrates common folder and file arrangements for Python projects:
| Folder Name | Description |
|---|---|
| src | Contains main source code files, scripts, and modules. |
| tests | Includes test scripts, preferably using frameworks like unittest or pytest. |
| data | Houses datasets, CSV files, or other input data files used for analysis or processing. |
| docs | Contains documentation, README files, or design documents related to the project. |
| venv | Houses the virtual environment files, isolating project dependencies. |
| README.md | A markdown file providing an overview, instructions, and project details. |
Adopting this structure allows for straightforward navigation, easier dependency management, and scalable development practices, especially as projects grow in complexity.
Managing Virtual Environments in Visual Studio Code
Creating and managing virtual environments within VS Code ensures that project dependencies are isolated, preventing conflicts and simplifying environment setup. This is vital for maintaining consistent behavior across different projects and development setups.
- Open the integrated terminal in VS Code using Ctrl + ` (Windows/Linux) or Cmd + ` (macOS).
- Navigate to your project directory using the
cdcommand. - Create a virtual environment by executing:
python -m venv venv
which creates a folder named venv containing the isolated environment.
- Activate the virtual environment:
- On Windows:
.\venv\Scripts\activate - On macOS/Linux:
source venv/bin/activate
- On Windows:
- Once activated, install project dependencies using
pip installcommands. The environment will keep these packages separate from system-wide installations. - In VS Code, select the interpreter associated with your virtual environment by opening the Command Palette ( Ctrl + Shift + P) and choosing Python: Select Interpreter. From the list, pick the interpreter pointing to the venv folder.
Proper virtual environment management promotes reproducibility, reduces dependency conflicts, and ensures that your development setup remains consistent across different machines and team members.
Writing and Editing Python Code Effectively

Developing efficient and maintainable Python code is vital for any programmer aiming to produce high-quality software. Visual Studio Code offers a suite of powerful features that streamline the coding process, enhance code quality, and boost productivity. Understanding how to leverage these tools effectively within the editor can significantly reduce development time while improving code clarity and correctness.
This section explores the key features of Visual Studio Code that assist in writing, editing, and refining Python code. It includes practical techniques for producing clean, efficient code, utilizing helpful extensions and snippets, and mastering essential shortcuts and tools that facilitate a smooth coding workflow.
Features of Visual Studio Code that Aid Python Coding
Visual Studio Code is equipped with advanced capabilities designed to support Python developers at every step of coding. Two of the most prominent features are IntelliSense and linting, which play a crucial role in maintaining high coding standards and reducing errors.
IntelliSense: Provides intelligent code completions, parameter info, quick info, and member lists as you write. This accelerates coding by suggesting relevant variables, functions, and classes, reducing typos and syntax errors.
Linting: Analyzes your code in real-time, flagging potential issues such as stylistic inconsistencies, semantic errors, or probable bugs based on configured linting tools like Pylint, Flake8, or Pyright. Linting helps enforce coding standards and improves code readability.
Additional features include syntax highlighting, code navigation, and integrated debugging, all of which create a more productive and error-free development environment.
Techniques for Writing Clean, Efficient Python Code
Writing high-quality Python code within Visual Studio Code involves adopting best practices and making full use of the editor’s functionalities. Consistently applying these techniques results in code that is easier to read, maintain, and optimize.
- Adopt PEP 8 Style Guidelines: Configure your editor with formatting extensions such as “Python extension” by Microsoft, which includes auto-formatting features aligning with PEP 8 standards, ensuring consistent indentation, spacing, and line length.
- Use Descriptive Naming Conventions: Choose meaningful variable, function, and class names that reflect their purpose, enhancing code clarity and reducing confusion.
- Write Modular Code: Break down complex tasks into smaller, reusable functions and classes. Use Visual Studio Code’s code folding feature to manage large code files effectively.
- Leverage Code Snippets and Extensions: Utilize predefined snippets for common code patterns (e.g., class definitions, loops) to speed up coding. Install extensions such as “Python Snippets” to access a rich library of reusable code templates.
- Implement Comments and Docstrings: Document your code using comments and docstrings to clarify logic and facilitate future modifications. Visual Studio Code supports quick documentation generation through extensions like “Python Docstring Generator.”
Ensuring code efficiency also involves profiling and refactoring. Use tools integrated with Visual Studio Code, such as the Python extension’s debugger, to identify bottlenecks and improve performance.
Using Code Snippets and Extensions to Enhance Productivity
Code snippets and extensions are invaluable for streamlining coding tasks, reducing repetitive work, and maintaining consistency across projects. Visual Studio Code’s marketplace offers numerous tools tailored for Python development that can significantly boost productivity.
- Code Snippets: Predefined templates for common coding structures allow you to insert complete code blocks with a few keystrokes. Customize snippets to match your coding style or project requirements.
- Extensions: Install extensions such as “Python,” “Pylance,” “AutoDocstring,” and “Python Test Explorer” to enable features like intelligent code completion, advanced type checking, automatic documentation, and seamless testing workflows.
- Intelligent Auto-Completion: Extensions like Pylance enhance IntelliSense, providing more accurate and context-aware suggestions for functions, methods, and variables.
- Refactoring Tools: Utilize extension-powered refactoring capabilities to rename variables, extract methods, or reorganize code efficiently without risking errors.
By integrating snippets and extensions into your workflow, you can write more consistent, error-free code faster, freeing up time for problem-solving and creative development.
Essential Code Editing Shortcuts and Tools
Mastering keyboard shortcuts and core tools in Visual Studio Code accelerates coding and editing tasks. Below is a list of essential shortcuts and features that every Python developer should incorporate into their workflow:
- Auto-Complete (Ctrl + Space): Trigger IntelliSense suggestions manually.
- Go to Definition (F12): Quickly navigate to the definition of functions, classes, or variables.
- Peek Definition (Alt + F12): View the definition inline without leaving the current context.
- Rename Symbol (F2): Refactor variable or function names across the project seamlessly.
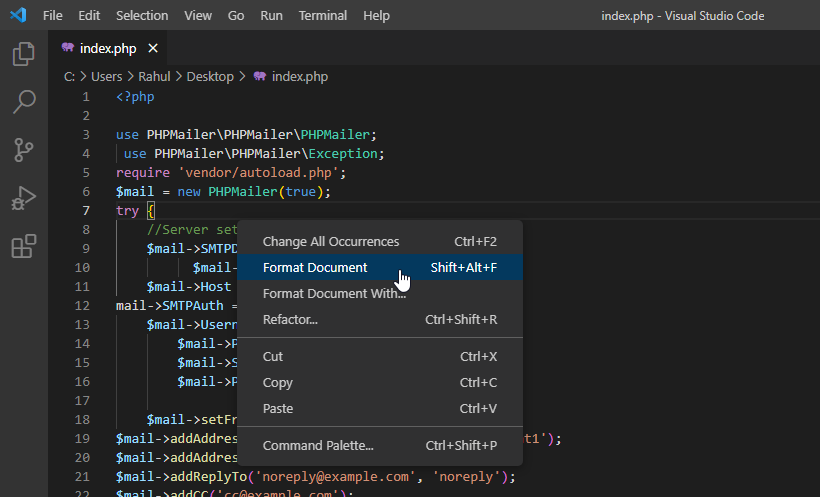
- Format Document (Shift + Alt + F): Auto-format code according to configured style guidelines.
- Comment/Uncomment Lines (Ctrl + /): Toggle comments on selected lines.
- Multi-Cursor Editing (Alt + Click): Place multiple cursors for simultaneous editing.
- Code Folding (Ctrl + Shift + [ / ]): Collapse or expand code blocks for better navigation.
- Run Selected Code (Shift + Enter in the integrated terminal): Execute specific code snippets without running entire files.
- Open Command Palette (Ctrl + Shift + P): Access all commands and extensions quickly.
Tools like the integrated debugger, Git version control, and terminal access are also integral to an efficient editing environment, enabling a seamless development process from coding to deployment.
Running and Debugging Python Scripts

Mastering the execution and troubleshooting of Python scripts within Visual Studio Code is essential for efficient development. Properly running your code allows you to verify functionality, while debugging tools help identify and resolve issues swiftly. Visual Studio Code provides an integrated environment that simplifies these processes, enabling developers to test and refine their code seamlessly.
Understanding how to run scripts directly from the editor, set breakpoints, and utilize the debugger effectively can significantly enhance your programming workflow. These skills enable you to pinpoint errors, analyze code behavior step-by-step, and implement solutions efficiently, contributing to a more productive development experience.
Executing Python Scripts in Visual Studio Code
The ability to run Python scripts directly from Visual Studio Code streamlines the development process and allows for immediate testing. The environment supports multiple methods for executing scripts, ensuring flexibility based on user preferences or specific project requirements.
- Using the Run Button: Located at the top right of the editor window, the green triangle icon allows you to execute the current script with a single click. Ensure the active file is a Python script (.py). When clicked, Visual Studio Code runs the script using the default Python interpreter configured in your workspace.
- Using the Integrated Terminal: Open the terminal within Visual Studio Code by selecting Terminal > New Terminal. Navigate to your script’s directory using the
cdcommand. Execute the script by typingpython filename.py(orpython3 filename.pydepending on your system). This method offers more control, especially when passing command-line arguments. - Using the Debug Panel: Initiate execution via the debugger by clicking on the Run and Debug icon on the sidebar. Select Run Python File from the options, which executes your script with debugging capabilities enabled.
Setting Breakpoints and Using the Debugger
Breakpoints are critical for pausing program execution at specific points, allowing detailed inspection of variable states, call stacks, and flow logic. Visual Studio Code’s debugger offers a robust set of tools to facilitate troubleshooting and fine-tuning your code.
- Adding Breakpoints: Click in the gutter (the space next to line numbers) to the left of the code line where you want the program to pause. A red dot appears, indicating an active breakpoint. You can set multiple breakpoints at different locations for comprehensive debugging.
- Starting the Debug Session: Click the Run and Debug icon on the sidebar and select Start Debugging. The debugger runs your script, halts at the first breakpoint, and highlights the current line.
- Inspecting Variables and Call Stack: During paused execution, utilize the Variables window to examine current values, and the Call Stack panel to understand the sequence of function calls leading to the current point.
- Stepping Through Code: Use the toolbar buttons to step over, into, or out of functions, or to continue execution until the next breakpoint. These controls allow precise navigation through your code.
Organizing Debugging Workflows with Procedures and Visual Aids
Structured debugging workflows enhance efficiency and reduce the trial-and-error period during problem resolution. The following procedures and visual aids serve as efficient guides for systematic troubleshooting in Visual Studio Code.
- Identify the Issue: Begin by reproducing the problem with a clear understanding of expected versus actual behavior. Use print statements or logging if necessary to gather preliminary insights.
- Set Strategic Breakpoints: Place breakpoints at key locations—such as before suspected errors or complex conditionals—to isolate problematic code sections.
- Run Debugger and Analyze: Start the debugging session, monitor variable states, and observe flow control. Use stepping features to trace the program execution line-by-line if needed.
- Interpret Error Messages: Pay close attention to error messages or exceptions displayed in the debugger console. These messages often pinpoint the source of errors, whether syntax issues, type mismatches, or runtime exceptions.
- Apply Fixes and Repeat: Modify the code based on insights gathered, remove or adjust breakpoints as necessary, and rerun debugging sessions to verify fixes.
| Common Error Types | Typical Causes | |
|---|---|---|
| SyntaxError | Incorrect syntax, missing colons, parentheses, or indentation issues. | Check the specific line mentioned in the error, verify syntax rules, and ensure consistent indentation. |
| NameError | Usage of undefined variables or misspelled names. | Ensure variables are defined before use, and confirm correct spelling and case sensitivity. |
| TypeError | Operations on incompatible data types. | Use type-checking functions (like type()) before operations, and convert data types if necessary. |
| IndentationError | Incorrect indentation levels within code blocks. | Maintain consistent indentation style, preferably 4 spaces, and review nested blocks carefully. |
Effective debugging involves a combination of strategic breakpoint placement, careful analysis of error messages, and iterative code refinement. Visual Studio Code’s debugging tools empower developers to diagnose and solve issues systematically, ultimately leading to more robust Python scripts.
Utilizing Version Control with Python Projects
Implementing version control within Python development projects enhances collaboration, maintains code integrity, and allows for efficient tracking of changes over time. Visual Studio Code offers seamless integration with Git, making it a powerful environment for managing your Python codebases effectively. Proper utilization of version control workflows ensures that development proceeds smoothly, especially within team settings, and supports best practices such as code reviews and branching strategies.
In this section, we explore how to integrate Git into Visual Studio Code, create repositories, manage commits, and utilize branching and merging workflows to facilitate collaborative coding and maintain a clean project history.
Integrating Git within Visual Studio Code for Python Projects
Visual Studio Code has built-in Git support, enabling developers to perform version control operations directly from the editor interface. To begin, ensure that Git is installed on your system. Once installed, VS Code automatically detects Git repositories and provides features such as source control panels, diff views, and commit management.
To initialize Git in your Python project, open the command palette (Ctrl+Shift+P or Cmd+Shift+P), then select ‘Git: Initialize Repository.’ This creates a new Git repository in your project folder. The Source Control icon in the activity bar displays the current repository status, showing untracked files, modifications, and staged changes.
Creating Repositories and Committing Changes
Managing code effectively requires creating repositories for your projects and regularly committing changes. After initializing a repository, you can stage files by clicking the ‘+’ icon next to them in the Source Control panel or by using the command palette with ‘Git: Stage All.’
Committing involves providing a descriptive message summarizing the changes made, enhancing traceability. Use the input box at the top of the Source Control view to enter your commit message, then click the checkmark icon or press Ctrl+Enter (Cmd+Enter on Mac) to commit. This process records the current state of your code, enabling rollback or comparison later.
Tip: Commit frequently with clear messages to keep your project’s history meaningful and manageable.
Branching and Merging Workflows with Visual Diagrams
Branching allows multiple developers to work on different features or bug fixes simultaneously without interfering with each other’s code. Visual Studio Code supports creating, switching, and managing branches through the Source Control interface or command palette commands such as ‘Git: Create Branch’ and ‘Git: Switch Branch.’
Visual diagrams illustrate that branches diverge from the main development line (main or master), allowing isolated work on features. When a feature is complete, it can be merged back into the main branch, consolidating changes. Merging can be performed via the ‘Git: Merge Branch’ command, which incorporates selected branch changes into the current branch.
| Workflow Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Branch Creation | Create a new branch for a feature or fix to isolate work from the main codebase |
| Development | Make changes within the feature branch, committing regularly to track progress |
| Pull Updates | Keep the feature branch up to date with the main branch to minimize merge conflicts |
| Merge | Integrate the feature branch back into the main branch once complete, resolving conflicts as needed |
Best Practices for Collaborative Coding and Code Reviews
Effective collaboration hinges on organized workflows and thorough code reviews. Teams should adopt branching models like GitFlow or GitHub Flow to manage feature development, bug fixes, and releases systematically. Pull requests (PRs) serve as checkpoints where team members can review code before integration.
Utilize Visual Studio Code extensions such as GitHub Pull Requests and Issues to facilitate review processes directly within the editor. Encourage detailed PR descriptions, inline comments, and constructive feedback. Regularly updating local branches, resolving conflicts promptly, and maintaining clear commit histories support a healthy collaborative environment and improve overall code quality.
Enhancing Python Development with Extensions and Tools

Optimizing your Python development experience in Visual Studio Code involves leveraging a variety of extensions and tools that streamline coding, testing, and project management. These enhancements not only improve productivity but also ensure code quality and consistency across projects. By customizing your editor with the right set of extensions, themes, linters, and formatters, you can create a tailored environment that aligns with your workflow and coding standards.
In this section, we explore popular VS Code extensions specifically designed for Python development, methods for personalizing your editor, and procedures to automate essential tasks like code formatting and testing. Incorporating these tools into your workflow can significantly elevate your efficiency and code maintainability.
Popular Visual Studio Code Extensions for Python Development
Choosing the right extensions is crucial for a productive Python development environment. The most widely used and recommended extensions include:
- Python: Developed by Microsoft, it provides core Python language support, IntelliSense, linting, debugging, and code navigation.
- Pylance: A fast and feature-rich language support extension that offers improved IntelliSense, type checking, and code analysis based on Microsoft’s Pyright type checker.
- Jupyter: Enables seamless integration of Jupyter Notebooks within VS Code, facilitating data analysis, visualization, and interactive coding.
- Black Formatter: Integrates the Black code formatter, encouraging consistent code style across projects for better readability and maintenance.
- Flake8: A linting tool that combines PEP8 checks, pyflakes, and McCabe complexity to identify potential issues and enforce coding standards.
- GitLens: Enhances version control capabilities by providing detailed insights into Git history, authorship, and code annotations directly within the editor.
Customizing the Editor with Themes, Linters, and Formatters
Personalization of your coding environment enhances focus and efficiency. Customization involves selecting themes for visual comfort, configuring linters to enforce coding standards, and setting up formatters to automatically maintain code style.
To customize your VS Code environment effectively:
- Themes: Access the Extensions marketplace and install preferred themes such as “Dark+,” “One Dark,” or “Solarized.” To switch themes, navigate to File > Preferences > Color Theme and select your choice. Themes reduce eye strain and improve focus during long coding sessions.
- Linters: Configure linters like Flake8 or Pylint by installing their extensions and setting preferences in your workspace settings. For instance, enabling Flake8 involves installing the extension and adding the line
“python.linting.flake8Enabled”: true
in your settings.json.
- Formatters: Install formatters such as Black or autopep
8. Activate automatic formatting on save by adding:
“editor.formatOnSave”: true
in your settings. This ensures your code adheres to the selected style without manual effort.
Comparison of Popular Extensions for Python Development
Understanding extension functionalities and installation procedures helps streamline setup and usage. Below is a comparison table highlighting key aspects:
| Extension | Primary Functionality | Installation Method | Configuration Highlights |
|---|---|---|---|
| Python | Core language support, debugging, IntelliSense | Search in Extensions marketplace > Install | Set interpreter path, configure linting and formatting options in settings |
| Pylance | Enhanced IntelliSense and type checking | Install via Extensions marketplace | Enable in settings; adjust type checking level |
| Jupyter | Notebook integration, interactive coding | Install via Extensions marketplace | Open notebooks, run cells, visualize data within VS Code |
| Black Formatter | Automatic code formatting | Install extension; configure settings.json for format on save | Set “editor.defaultFormatter” to ms-python.black-formatter |
| Flake8 | Code linting and standards enforcement | Install extension; enable in settings | Configure max line length, ignore specific warnings in settings.json |
| GitLens | Advanced version control insights | Install via Extensions marketplace | Customize blame annotations, history views, and inline code insights |
Automating Code Formatting and Testing Procedures
Automation enhances consistency and reduces manual effort during development. Automating code formatting and testing involves configuring VS Code to perform these tasks seamlessly, often triggered by save actions or integrated with version control workflows.
To automate code formatting:
- Install a formatter extension such as Black or autopep8.
- Add the following configuration to your settings.json to format code automatically on save:
“editor.formatOnSave”: true
- Set the default formatter by including:
“editor.defaultFormatter”: “ms-python.black-formatter”
For automated testing, integrate testing frameworks like pytest by installing the corresponding extension or configuring tasks:
- Ensure pytest is installed in your environment.
- Configure a debugging or task runner to execute tests with commands such as pytest.
- Use the built-in testing features of VS Code to run, debug, and monitor test results interactively.
Automating these processes ensures that your code maintains high standards of quality and style, with minimal manual intervention, ultimately streamlining your development workflow.
Learning Resources and Community Support
Embarking on Python programming is greatly enhanced by accessing quality learning resources and engaging with active community support. These elements provide guidance, practical advice, and ongoing motivation to deepen your understanding and solve challenges efficiently. Leveraging tutorials, documentation, and community forums helps both beginners and experienced developers stay current with best practices and emerging trends in Python development.
Engaging with the Python community and utilizing available resources also fosters continuous learning, collaboration, and troubleshooting. Whether you’re tackling setup issues, exploring new libraries, or contributing to open-source projects, strong support networks and curated learning materials are invaluable assets in your programming journey.
Recommended Tutorials, Documentation, and Forums for Python Learners
Access to comprehensive tutorials, official documentation, and active forums accelerates learning by providing practical examples, clear explanations, and peer support. These resources are essential for troubleshooting, understanding new concepts, and staying motivated throughout your development experience.
- Official Python Documentation: The definitive resource for Python’s syntax, built-in functions, standard libraries, and language updates, providing thorough explanations and examples.
- Real Python: Offers beginner to advanced tutorials, articles, and video courses that cover a wide spectrum of Python topics, emphasizing real-world applications.
- Stack Overflow: A vibrant community where developers ask questions and share solutions on common and complex Python issues, fostering collaborative problem-solving.
- Python Forum: An official discussion platform dedicated to Python programming, where users discuss issues, share projects, and seek advice in a structured manner.
- W3Schools Python Tutorial: An accessible starting point for beginners, offering interactive lessons and code examples to grasp fundamental concepts.
Strategies for Troubleshooting Common Setup Problems
Encountering setup issues is common during initial Python or Visual Studio Code configuration. Systematic troubleshooting strategies can streamline problem resolution and minimize frustration.
- Verify that Python is correctly installed by running
python –version
in your command prompt or terminal to ensure the expected version appears.
- Check the PATH environment variable to confirm that Python’s installation directory is included, enabling command-line access.
- Ensure that Visual Studio Code has the Python extension installed and enabled, which provides IntelliSense and debugging support.
- Review the Integrated Terminal settings in VS Code to confirm it uses the correct shell environment compatible with your system (e.g., Command Prompt, PowerShell, Bash).
- Consult the output and debug consoles in VS Code for error messages or warnings that pinpoint configuration issues.
- Search for specific error messages online—most setup problems have documented solutions on forums like Stack Overflow.
Participating in Developer Communities and Open-Source Projects
Active engagement in Python developer communities and open-source projects enriches your learning experience, exposes you to diverse coding styles, and enhances your professional network. These interactions foster collaboration, mentorship, and the opportunity to contribute meaningfully to software used worldwide.
- Join Online Communities: Platforms such as Reddit’s r/learnpython, Python Discord servers, and mailing lists facilitate real-time discussion, resource sharing, and peer support.
- Contribute to Open-Source Projects: Platforms like GitHub host numerous Python projects seeking contributors. Starting with issues labeled “good first issue” provides manageable entry points.
- Attend Meetups and Conferences: Events like PyCon or local Python meetups enable face-to-face networking, knowledge exchange, and exposure to innovative projects.
- Engage in Coding Challenges: Platforms like LeetCode, HackerRank, and Codewars offer challenges that foster problem-solving skills and community interaction.
Organized List of Online Courses and Resources with Brief Descriptions
Structured online courses and curated resources provide comprehensive learning pathways suited to various skill levels, from novice to expert. These courses often include videos, exercises, and certification options to reinforce skills and track progress.
| Resource | Description | Level |
|---|---|---|
| Coursera – Python for Everybody | An in-depth course by the University of Michigan covering Python basics, data structures, and web access, ideal for beginners seeking foundational knowledge. | Beginner |
| edX – Introduction to Computer Science and Programming Using Python | Offered by MIT, this course combines programming fundamentals with problem-solving and algorithmic thinking, suitable for beginners and intermediate learners. | Beginner to Intermediate |
| Udemy – Complete Python Developer in 2023: Zero to Mastery | A comprehensive course that covers Python syntax, libraries, frameworks, and real-world projects, aimed at aspiring developers. | Beginner to Advanced |
| Codecademy – Learn Python 3 | Interactive lessons focusing on syntax, functions, and data structures, providing hands-on practice for beginners. | Beginner |
| Real Python | Offers tutorials, articles, and courses on a broad range of topics, emphasizing practical application and best practices. | All levels |
Conclusion
Mastering how to code in Python using Visual Studio Code editor empowers you to develop, debug, and manage your projects seamlessly within a versatile environment. Armed with the right setup and tools, you can accelerate your learning curve and produce high-quality Python code efficiently. Embrace these foundational skills to elevate your programming journey and unlock new possibilities in software development.