Deploying a React project to Netlify with a custom domain offers a seamless way to showcase your application with a professional touch. The process involves preparing your React app for production, setting up a Netlify account, configuring deployment settings, and linking your custom domain through DNS management. This guide provides clear, step-by-step instructions to help you successfully launch your React project on Netlify, ensuring it is secure, responsive, and easily maintainable.
Preparing Your React Project for Deployment
Ensuring your React application is production-ready is essential for optimal performance, fast load times, and a seamless user experience. Proper preparation includes building the project with the correct commands, optimizing assets, and organizing the output for deployment. This process not only improves efficiency but also ensures compatibility across various hosting environments like Netlify.
In this section, we will explore the critical steps involved in preparing your React project for deployment, focusing on build processes, optimization techniques, and a clear, step-by-step guide to streamline the deployment workflow.
Running the Build Process in React
The core step in preparing a React project for deployment involves creating an optimized production build. React’s build command compiles the source code into static files suitable for hosting. The key command is:
npm run build
This command triggers the React build script defined in your project’s package.json, which typically uses tools like Webpack or Vite under the hood to generate a production bundle. The output is a folder named build that contains minified, optimized JavaScript, CSS, and static assets ready to be deployed.
The build folder is crucial because it contains the final version of your application, free from development-specific features like source maps and hot module replacement. This ensures the application loads faster and performs efficiently in a production environment.
Optimizing React for Production
To maximize the performance and responsiveness of your React application, several optimization techniques should be employed before deployment. These techniques reduce the size of assets, improve load times, and enhance user experience in real-world scenarios with varying network speeds and device capabilities.
- Code splitting: Dividing your application into smaller chunks that load on demand, decreasing initial load time. Implemented using React’s
React.lazy()andSuspensefor dynamic import of components. - Minification: Compressing JavaScript and CSS files to reduce their size, which is inherently handled by the production build process, but can be complemented with additional tools for further compression.
- Tree shaking: Eliminating unused code during the build process to minimize bundle size, which is typically enabled in production mode with modern bundlers like Webpack.
- Image optimization: Compressing images, serving modern formats like WebP, and implementing lazy loading strategies to improve load times and reduce data usage.
- Environment variables: Setting environment variables to manage different configurations for development and production, ensuring sensitive data remains secure and that production-specific settings are applied.
Implementing these optimizations ensures that your React app is not only functional but also efficient and optimized for delivering a high-quality user experience across diverse devices and network conditions.
Step-by-Step Guide to Prepare Your React Project
Follow these steps to prepare your React project for deployment effectively, ensuring all necessary configurations and optimizations are in place:
- Update dependencies: Ensure all packages are up-to-date to benefit from the latest features and security patches.
- Configure environment variables: Create a
.envfile in the root of your project to set production-specific variables, such as API endpoints or feature flags. - Implement code splitting: Use
React.lazy()andSuspenseto load components dynamically, especially for large modules. - Perform a production build: Run the build command to generate the optimized static files.
- Test the build locally: Use a local server to verify the production build functions correctly before deployment.
- Review and optimize assets: Minimize images, verify CSS and JavaScript minification, and confirm lazy loading behaviors.
npm updateREACT_APP_API_URL=https://api.yourdomain.comconst LazyComponent = React.lazy(() => import('./LazyComponent'));npm run buildnpm install -g serve
serve -s buildFollowing this structured approach ensures your React project is thoroughly prepared, optimized, and ready for deployment to hosting platforms like Netlify, providing users with a fast, reliable application experience.
Setting Up a Netlify Account and Connecting Your Repository
Establishing a Netlify account and linking it with your version control system is a fundamental step in deploying your React project efficiently. This process ensures seamless integration, automated deployments, and streamlined management of your application’s hosting environment. Proper configuration of your account and repositories can significantly reduce deployment errors and facilitate collaboration among team members.
Netlify offers a user-friendly platform that simplifies deployment workflows for static sites and single-page applications like React. By connecting your GitHub repository, you enable Netlify to automatically build and deploy your project whenever updates are pushed to your designated branch. This integration ensures your live site remains synchronized with your development process, allowing for rapid iteration and continuous delivery.
Creating a Netlify Account and Linking with GitHub
To begin, you must first create a free Netlify account and establish a connection with your preferred version control system, such as GitHub. The following steps Artikel the process:
- Sign Up on Netlify: Navigate to Netlify’s official website . Click on the “Sign up” button and register using your email address or authenticate via GitHub, GitLab, or Bitbucket for quicker access.
- Authorize Netlify to Access Your Repository: During registration, select the option to connect with your preferred Git provider. You will be prompted to authorize Netlify to access your repositories. Ensure you grant permissions to the relevant repositories to enable smooth deployment management.
- Configure Repository Access: After authorization, Netlify will display your repositories. Select the repository hosting your React project. Confirm that the repository has the appropriate access rights, especially if working within teams, to prevent deployment issues due to permission restrictions.
It is advisable to organize repository access through team management features within your version control platform to maintain proper control over deployment rights and collaboration permissions. Restrict deployment privileges to trusted team members to avoid accidental or malicious changes that could affect your live site.
Connecting Your React Repository to Netlify and Selecting the Branch
Once your account is set up and linked with your repository, the next step involves configuring the deployment settings in Netlify. This includes selecting the specific branch of your repository that you wish to deploy. Here are the key considerations and steps:
- Initiate a New Site Deployment: In the Netlify dashboard, click on “New site from Git” to begin the connection process.
- Select Your Repository: Choose the repository that contains your React project from the list of connected accounts and repositories.
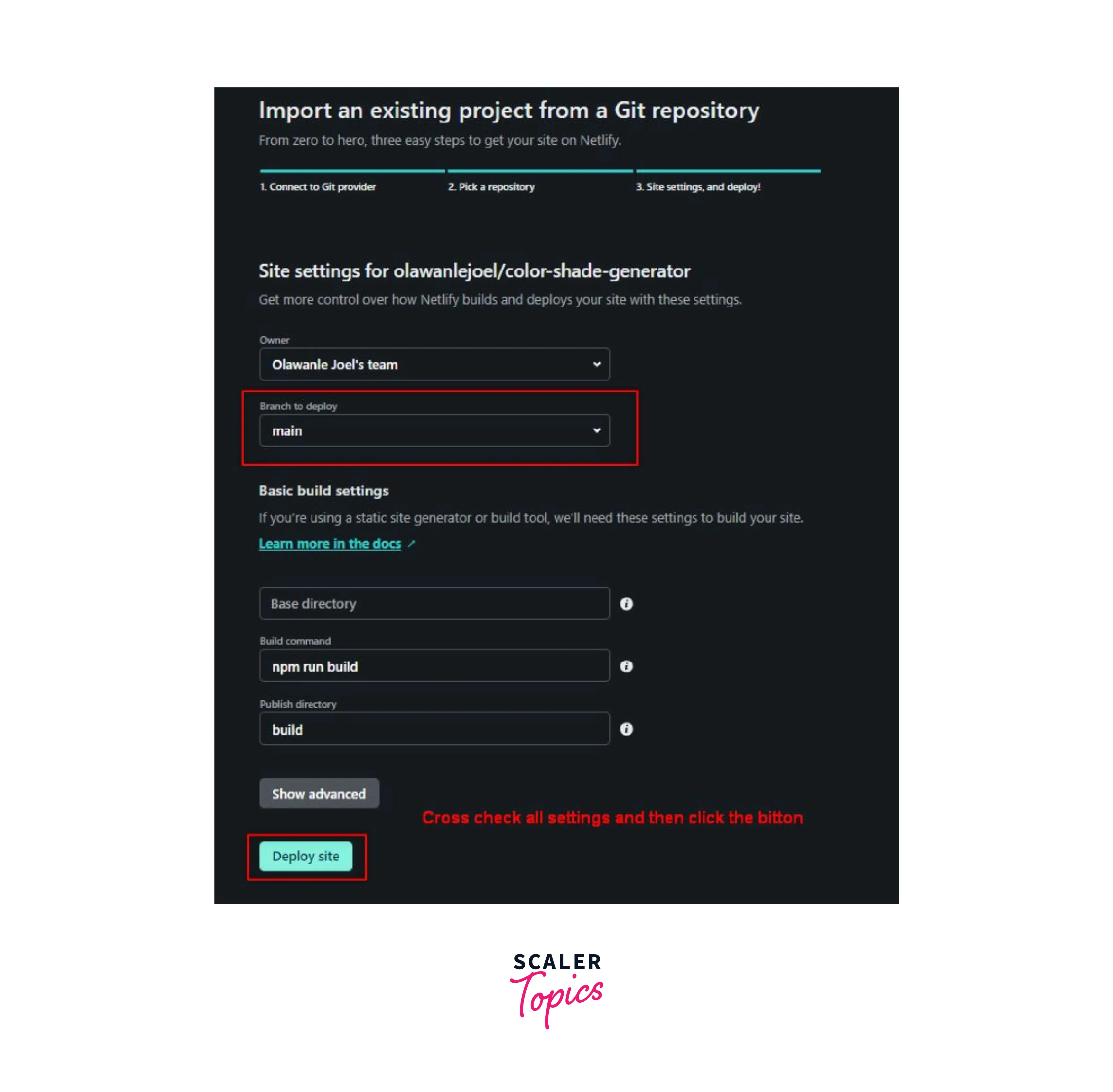
- Choose the Branch: Netlify will prompt you to select a branch, commonly “main” or “master,” which contains the latest stable code for deployment. If you follow a branching strategy like GitFlow, select the branch designated for production or release.
- Configure Build Settings: Ensure that the build command (e.g., “npm run build”) and the publish directory (usually “build”) are correctly specified. These settings align with your React project’s build process to generate a production-ready static site.
Adopting best practices for repository management involves maintaining a clear branch strategy, using descriptive branch names, and restricting deployment rights to prevent unintended updates. Regularly review access permissions through your version control platform’s settings, ensuring only authorized personnel can trigger deployments or modify connection settings.
Configuring Deployment Settings on Netlify
Proper configuration of deployment settings on Netlify is essential for ensuring your React application builds and serves correctly. This step involves specifying the build commands and the directory where the production-ready files are generated, enabling a smooth deployment process and facilitating automatic updates with each code push.
Netlify provides an intuitive dashboard that allows you to customize your deployment parameters easily. Correctly setting the build command and publish directory ensures that your project compiles without errors and is served correctly to users. Additionally, enabling continuous deployment automates updates, making your workflow more efficient and reducing manual intervention. Troubleshooting common issues related to build configuration ensures minimal downtime and quick resolution of deployment errors.
Specifying Build Commands and Publish Directory
Accurately defining the build command and publish directory within Netlify’s deployment settings is a crucial initial step. This configuration directs Netlify on how to compile your React project and where to find the files to serve on your website.
The typical setup for a React project involves the following configurations:
| Field | Example / Explanation |
|---|---|
| Build command | npm run build |
| Publish directory | build |
Note: The build command ‘npm run build’ initiates the production build of your React app, which generates static files in the ‘build’ directory by default. Ensure your package.json contains the correct build script.
To set these configurations:
- Log in to your Netlify dashboard and navigate to your site’s settings.
- Locate the ‘Build & deploy’ section and click on ‘Continuous deployment’.
- Under ‘Build settings,’ specify the build command as
npm run build. - Set the publish directory to
build. - Save the changes to apply the configuration.
Enabling Continuous Deployment and Automatic Updates
Continuous deployment is a powerful feature that automatically triggers a new build and deploys your site whenever you push changes to your connected repository. This minimizes manual effort and ensures your website remains up-to-date with the latest codebase.
To enable this feature:
- Connect your repository (GitHub, GitLab, or Bitbucket) to your Netlify project, if not already done.
- In the ‘Build & deploy’ section, verify that your repository is linked under ‘Continuous deployment.’
- Ensure the branch you want to deploy from (e.g., main or master) is selected.
- Enable automatic deploys by toggling the ‘Deploy site automatically’ option.
- Configure build settings as discussed earlier, then save the configuration.
With this setup, every push to the specified branch triggers Netlify to automatically build and deploy your React project, streamlining updates and reducing deployment delays.
Troubleshooting Common Deployment Errors
Despite careful configuration, deployment errors can occasionally occur. Recognizing and resolving these issues quickly is vital for maintaining a smooth deployment pipeline.
Some frequent errors include:
- Build command not recognized or failing: Ensure that your package.json contains the correct build script, such as
"build": "react-scripts build". Check the build logs for specific error messages. - Incorrect publish directory: Verify that the output folder specified (commonly
build) exists after running the build command. If your build outputs to a different folder, update the publish directory accordingly. - Dependency issues: Make sure all dependencies are installed locally and listed correctly in your package.json file. Running
npm installbefore build helps mitigate this problem. - Environment variables missing: Some projects require environment variables for production builds. Set these in Netlify’s environment variable settings under ‘Site settings.’
Tip: Always review the build logs in Netlify for detailed error messages. Running the build process locally (via
npm run build) can also help identify issues before deploying.
Setting Up a Custom Domain on Netlify
Assigning a custom domain to your deployed React project enhances its professionalism and brand recognition. Netlify provides a seamless process for adding and managing custom domains, ensuring your website is accessible via your preferred web address. This section details the steps to register your custom domain, connect it to Netlify, and properly configure DNS settings for optimal performance and security.
By correctly configuring DNS records and verifying ownership, you ensure that your domain points precisely to your Netlify deployment. Additionally, SSL/TLS certificates are automatically provisioned through Let’s Encrypt to secure your website with HTTPS, boosting user trust and search engine ranking.
Registering and Adding a Custom Domain in Netlify
To start, you need to acquire your domain from a domain registrar, such as GoDaddy, Namecheap, or Google Domains. Once you have your domain, adding it to Netlify is straightforward and involves the following steps:
- Log into your Netlify dashboard and navigate to your site’s settings.
- Select the “Domain management” section and click on “Add custom domain.”
- Enter your domain name (e.g., www.yourdomain.com) and verify its availability.
- Netlify will check if the domain is already connected or needs configuration. Confirm the addition to proceed.
After adding the domain, Netlify will generate DNS records that need to be configured at your domain registrar to point the domain to Netlify’s servers.
Configuring DNS Records at Your Domain Registrar
Proper DNS setup is critical for ensuring your custom domain correctly directs visitors to your Netlify-hosted site. The process involves updating DNS records at the registrar’s control panel, depending on your domain’s existing configuration:
- A Records: These records point your domain directly to Netlify’s IP addresses. Use this method if you prefer to set up your root domain (e.g., yourdomain.com). Netlify’s current IP addresses are:
- CNAME Records: For subdomains (e.g., www.yourdomain.com), create a CNAME record that points to your Netlify site URL (e.g., your-site.netlify.app). This allows for easier management and flexibility.
- NS Records: If you want Netlify to manage your DNS entirely, change your domain’s nameservers to Netlify’s DNS servers. However, this approach is typically used when leveraging Netlify’s DNS management features exclusively.
104.198.14.52, 104.198.14.53
To update these records:
- Access your domain registrar’s DNS management panel.
- Add or modify the relevant A or CNAME records according to Netlify’s instructions.
- Save the changes and wait for DNS propagation, which can take from a few minutes up to 48 hours, depending on your registrar.
Verifying Domain Ownership and Ensuring HTTPS
Once DNS records propagate, Netlify automatically verifies domain ownership and provisions SSL/TLS certificates via Let’s Encrypt. To confirm this process:
- Navigate to your site’s “Domain management” section in Netlify.
- Check the status of your custom domain; it should indicate “Verified” once DNS records are correctly set.
- Ensure that “Secure” or “SSL/TLS certificate” status shows as active. If not, you can trigger a manual SSL certificate provisioning by clicking the relevant button.
- Verify HTTPS accessibility by visiting your domain with “https://” in the URL. Your browser should display a padlock icon indicating a secure connection.
“Automatic SSL certificate provisioning by Netlify simplifies securing your website, providing HTTPS without additional configuration.”
It is advisable to periodically verify your SSL status and DNS configurations to prevent service disruptions. Proper setup ensures a secure, reliable, and professional online presence for your React application.
Managing DNS Records and Propagation

When configuring a custom domain for your React project hosted on Netlify, managing DNS records effectively is crucial to ensure that your domain correctly points to your site and that SSL certificates are issued securely. Proper handling of DNS records helps prevent downtime, delays in domain propagation, and SSL-related issues that could hinder your website’s accessibility and security.
Effective management involves understanding the different types of DNS records required, organizing them appropriately within your domain registrar’s dashboard, and monitoring the propagation process to confirm that your domain is properly linked to your Netlify deployment. Troubleshooting common DNS issues ensures a smooth transition and optimal performance for your site’s visitors.
Types of DNS Records Needed for Custom Domain Setup with Netlify
Setting up your custom domain involves configuring several DNS record types. Each type serves a specific purpose in establishing a secure, reliable connection between your domain and your Netlify-hosted site:
| Record Type | Description | Common Use Case in Netlify Setup |
|---|---|---|
| A Record | Points your domain or subdomain to a specific IP address. | Directs the root domain (e.g., example.com) to Netlify’s IP address if using IP-based pointing. |
| CNAME Record | Points your subdomain to another domain name, typically used for aliasing. | Points www.example.com to Netlify’s default domain (e.g., yoursite.netlify.app). |
| ALIAS or ANAME Record | Acts like an A record but for root domains, pointing to a hostname. | Used when DNS provider supports ALIAS or ANAME records to connect root domains to Netlify’s domain. |
| TXT Record | Stores text data for various purposes, including domain verification and SSL certification. | Verifies domain ownership for SSL issuance and DNS validation with Netlify. |
| CAA Record | Specifies which Certificate Authorities are permitted to issue SSL certificates for your domain. | Enhances security by restricting SSL certificate issuance to trusted CAs, ensuring SSL setup integrity. |
Organizing DNS Records in Various Domain Registrars and Checking Propagation Status
Each domain registrar’s interface varies but generally follows similar steps for managing DNS records. It’s essential to locate the DNS management section, often labeled as “DNS Settings,” “DNS Management,” or “Name Servers.” After adding or modifying records, understanding how to verify their status and propagation is equally important.
- Access your domain registrar’s control panel and navigate to the DNS management area.
- Input the necessary DNS records as specified by Netlify, ensuring correct record types, hostnames, and values.
- Save changes and wait for DNS propagation, which can take from a few minutes up to 48 hours depending on the registrar and DNS cache duration.
- Utilize online DNS checker tools, such as “WhatsMyDNS.net” or “DNSChecker.org,” to monitor the propagation status globally. Enter your domain name and the specific record type to verify if the changes have propagated correctly.
Tip: Ensure that TTL (Time To Live) settings are set to a lower value (e.g., 300 seconds) during initial setup to facilitate quicker propagation and easier troubleshooting.
Troubleshooting DNS Issues Affecting Domain Connection and SSL Certificates
DNS-related issues can cause delays or failures in domain connection and SSL certificate issuance. Common problems and their solutions include:
- Incorrect DNS Record Configuration: Double-check record types, hostnames, and target values. For example, ensure CNAME for www points to your Netlify domain correctly.
- Propagation Delays: Patience is key; DNS changes can take time to propagate globally. Use DNS checker tools to confirm when records are active.
- Cache Issues: Clear local DNS cache or try accessing your domain from different networks or devices to bypass cached outdated information.
- SSL Certificate Problems: If SSL isn’t issued promptly, verify DNS records, especially TXT records used for domain verification, are correctly set. Also, ensure your domain’s DNS provider supports required record types and that there are no conflicting records.
- Firewall or Security Settings: Some DNS providers or firewalls may block certain DNS queries. Review your DNS provider’s documentation or contact support if issues persist.
Regularly monitoring DNS status and following these troubleshooting steps can help resolve most issues promptly, ensuring your custom domain is successfully connected and secured with SSL on Netlify.
Verifying Deployment and Custom Domain Functionality
After completing the deployment process and configuring your custom domain, it is essential to verify that your React project is accessible, secure, and functioning correctly through the custom domain. Proper verification helps ensure a smooth user experience and confirms that your deployment setup is correctly configured without issues related to domain resolution or security certificates. This process involves checking accessibility, responsiveness, SSL certificate validity, and troubleshooting potential problems that may arise during deployment or domain configuration.Ensuring that your React application is accessible via the custom domain and performing thorough testing on various devices and browsers guarantees that the deployment was successful.
Confirming the SSL certificate’s validity and HTTPS security is crucial for protecting user data and building trust with your audience. Detecting and resolving common deployment or domain configuration issues early can save significant time and maintain website availability.
Accessing Your React Project via Custom Domain and Testing Responsiveness
To verify that your React project is correctly deployed and accessible through your custom domain, follow these steps:
Start by entering your custom domain URL into a web browser. If the deployment setup is accurate, the React application should load seamlessly, displaying your website’s homepage or designated landing page. Use different devices such as desktops, tablets, and smartphones to test responsiveness. Resize your browser window or use device simulation tools to ensure that the layout adapts appropriately across various screen sizes.
Confirm that interactive elements respond correctly and that navigation remains user-friendly on all devices.
Additionally, perform cross-browser testing by opening your website in popular browsers like Chrome, Firefox, Safari, and Edge. This helps identify any browser-specific issues related to rendering or functionality. Ensuring that the website loads promptly and displays correctly across platforms affirms successful deployment and domain configuration.
Checking SSL Certificate Validity and HTTPS Connection Security
Maintaining a secure HTTPS connection is vital for user trust and ranking. Confirming the validity of your SSL certificate involves:
- Visiting your website using the
https://protocol and observing the browser’s security indicators, such as a padlock icon in the address bar. - Clicking on the padlock icon to view detailed certificate information, including issuer and expiration date. The certificate should be issued by a recognized Certificate Authority (CA) and not be expired.
- Using online tools such as SSL Labs’ SSL Server Test to analyze your domain’s SSL configuration comprehensively. These tools provide insights into certificate validity, supported protocols, cipher suites, and potential vulnerabilities.
Ensure that your domain redirects all HTTP traffic to HTTPS, enforcing secure connections. This can be verified by attempting to access your site via http:// and confirming automatic redirection to the https:// version. A secure HTTPS connection guarantees data encryption and enhances user confidence.
Troubleshooting Common Deployment or Domain Configuration Problems
In cases where your website does not load correctly, displays security warnings, or encounters other issues, consider the following troubleshooting steps:
- Domain propagation delays: DNS changes can take up to 48 hours to propagate globally. Use DNS checker tools to confirm that your domain points to the correct Netlify IP addresses.
- Incorrect DNS records: Verify that your DNS records, especially CNAME or A records, are correctly configured to point to Netlify’s servers. An incorrect record can prevent your domain from resolving properly.
- SSL certificate issues: If the SSL certificate is invalid or not issued correctly, browsers may block access or display security warnings. Ensure that Netlify’s automatic SSL provisioning is complete and that the certificate is active.
- Caching problems: Browser cache or CDN caching might cause outdated content to display. Clear your browser cache or try accessing your site in incognito mode to see the latest deployment.
- Deployment errors: Review Netlify’s deployment logs for errors or warnings that might indicate build or deployment issues. Correct any errors and redeploy if necessary.
Regularly monitor your site’s status using browser developer tools, online SSL checkers, and DNS lookup services to ensure ongoing functionality and security. Addressing these issues promptly helps maintain a reliable, secure, and user-friendly website experience.
Additional Deployment Tips and Best Practices
Ensuring a smooth and secure deployment process for your React project involves following best practices that enhance maintainability, security, and flexibility. Implementing these strategies can help you manage environment settings effectively, handle deployment updates seamlessly, and maintain a reliable deployment environment on Netlify, especially when working with custom domains.Effective deployment management requires balancing ease of updates with security considerations. Proper handling of environment variables and secrets helps protect sensitive data such as API keys and service credentials, while strategic deployment procedures ensure minimal downtime and consistent user experience.
Keeping detailed records of deployment steps and utilizing tools for version control and rollback capabilities further strengthen your deployment workflow.
Managing Environment Variables and Secrets
Environment variables are crucial for configuring your React application during deployment without exposing sensitive information. When deploying on Netlify, leverage their built-in environment variable management feature to securely store API keys, database credentials, and other secrets. This avoids hardcoding sensitive data into your source code, which could be exposed in public repositories.To efficiently manage environment variables:
- Navigate to the Netlify dashboard of your site, then go to “Site Settings” > “Build & Deploy” > “Environment.”
- Define key-value pairs for all necessary secrets and configuration options.
- Access these variables within your React app via process.env, ensuring they are prefixed with REACT_APP_ to expose them during build time.
Remember to avoid exposing sensitive secrets to the client-side code unless explicitly necessary. For server-side secrets or backend components, consider deploying them separately or using serverless functions provided by Netlify.
Procedures for Rolling Back Deployments and Updating Custom Domain Settings
Maintaining control over your deployment lifecycle is essential for rapid recovery from errors and smooth domain management. Netlify offers versioning capabilities that allow you to revert to previous deploys if issues arise after a new deployment.To rollback:
- Open the Netlify dashboard and navigate to your site’s deploys page.
- Identify the previous stable deployment version listed under the deploy logs.
- Click on the “Publish” button associated with that deploy to revert your site to a known good state.
For updating custom domain settings, such as changing DNS records or adjusting SSL/TLS configurations:
- Access the “Domain management” section in Netlify’s dashboard.
- Make necessary DNS record modifications through your domain registrar, following Netlify’s guidelines for DNS setup.
- Update SSL/TLS settings if required, ensuring your site remains secure with HTTPS after the change.
Always verify the correctness of DNS propagation and SSL certificates after any changes to prevent disruptions.
Key Deployment Strategies and Best Practices
To optimize your React deployment process, consider adopting these core strategies:
Maintain version control: Use Git or similar tools to track changes and facilitate rollbacks. Tag releases for easy reference and deployment reproducibility.
Automate deployments: Configure continuous deployment pipelines using CI/CD tools integrated with Netlify for automatic deployment upon code pushes, minimizing manual intervention and reducing errors.
Secure secrets management: Store environment variables securely within Netlify’s environment settings, avoiding exposure in code repositories or logs.
Optimize build settings: Use production optimizations such as code minification, compression, and tree shaking to improve site performance.
Monitor deployment health: Regularly review deployment logs and site analytics to detect and resolve issues promptly. Utilize Netlify’s built-in analytics and monitoring tools.
Summary of Key Deployment Steps, Tools, and Best Practices
| Step / Aspect | Tools / Resources | Best Practices |
|---|---|---|
| Managing Environment Variables | Netlify Dashboard, process.env in React | Keep secrets secure, prefix with REACT_APP_, update via Netlify interface |
| Deploying New Versions | Git, Netlify Continuous Deployment | Tag releases, automate deployment pipelines, test before publishing |
| Rolling Back Deployments | Netlify Deploys History | Select previous deploy, publish to revert quickly, verify site integrity |
| Custom Domain Setup | DNS Registrar, Netlify Domain Settings | Update DNS records accurately, monitor propagation, renew SSL certificates |
| Site Monitoring and Maintenance | Netlify Analytics, External Monitoring Tools | Regularly review logs, implement performance optimizations, ensure security |
Last Word
By following these comprehensive steps, you can confidently deploy your React application to Netlify and connect it with a custom domain. This not only enhances your project’s credibility but also simplifies ongoing management and updates. With proper configuration and attention to DNS details, your React app will be accessible, secure, and ready to impress visitors worldwide.